Heart rate variability biofeedback to reduce anxiety in autism spectrum disorder - a mini review
- PMID: 38938467
- PMCID: PMC11208699
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1409173
Heart rate variability biofeedback to reduce anxiety in autism spectrum disorder - a mini review
Abstract
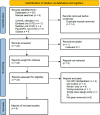
There is a reported high prevalence of anxiety in people with autism spectrum disorder. This mini review appraises existing research investigating heart rate variability biofeedback to help manage symptoms of anxiety in people with autism spectrum disorder. A thorough search of electronic databases was conducted to find relevant literature. Consultation with experts and a librarian helped develop search terms following the PICO framework. Five databases were searched, and screening was undertaken using Covidence software, with the process outlined in a PRISMA flowchart. The latest review showed positive short-term effects but there is a need for long-term follow-up. Future investigations should consider device type, training settings, and control interventions. Accurate heart rate variability assessment independent of biofeedback devices is crucial. Additional measures like cortisol assessment and user feedback are recommended for comprehensive evaluation. The findings highlight progress in the evidence base and offer insight to future directions.
Keywords: anxiety; autism spectrum disorder; digital health; heart rate variability biofeedback; intervention.
Copyright © 2024 Coulter, Donnelly, Yakkundi, McAneney, Barr and Kernohan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback to Treat Anxiety in Young People With Autism Spectrum Disorder: Findings From a Home-Based Pilot Study.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Aug 26;6(8):e37994. doi: 10.2196/37994. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 36018712 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated use of biofeedback and neurofeedback techniques in treating pathological conditions and improving performance: a narrative review.Front Neurosci. 2024 Mar 19;18:1358481. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1358481. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38567285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Biofeedback-Assisted Resilience Training for Traumatic and Operational Stress: Preliminary Analysis of a Self-Delivered Digital Health Methodology.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Sep 6;7(9):e12590. doi: 10.2196/12590. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019. PMID: 31493325 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of Biofeedback Interventions for Addressing Anxiety and Depression in Children and Adolescents with Long-Term Physical Conditions.Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2018 Sep;43(3):179-192. doi: 10.1007/s10484-018-9399-z. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2018. PMID: 29946920
References
-
- Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology . Heart rate variability. Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Eur Heart J. (1996) 17:354–81. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a014868 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources