The threshold effect of triglyceride glucose index on diabetic kidney disease risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: unveiling a non-linear association
- PMID: 38938513
- PMCID: PMC11208310
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1411486
The threshold effect of triglyceride glucose index on diabetic kidney disease risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: unveiling a non-linear association
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have confirmed that the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index, recognized as a reliable marker of insulin resistance, is an important risk factor for diabetic kidney disease (DKD). However, it is still unclear whether the DKD risk continues to increase linearly with the elevation of TyG index. This study aimed to thoroughly investigated the intrinsic relationship between TyG index and DKD risk in type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 933 patients with T2D in China, who were categorized into DKD and non-DKD groups and stratified by TyG index levels. Logistic regression analysis identified the independent risk factors for DKD. The association between DKD risk and TyG index was evaluated using the restricted cubic spline (RCS) curves analysis. The R package 'CatPredi' was utilized to determine the optimal cut-off point for the relationship between DKD risk and TyG index, followed by threshold effect analysis.
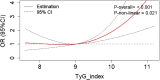
Results: The prevalence of DKD was 33.01%. After adjusting for confounding factors, TyG index was identified as a prominent clinical risk factor for DKD, showing the highest odds ratio (OR 1.57 (1.26 - 1.94), P<0.001). RCS analysis revealed a non-linear relationship with a threshold interval effect between the TyG index and DKD risk. When TyG index ≤ 9.35, DKD risk plateaued at a low level; however, when TyG index > 9.35, DKD risk increased gradually with rising TyG index. Among patients with TyG index > 9.35, each 1-unit increase was associated with a 1.94-fold increased DKD risk (OR=1.94 (1.10 - 3.43), P=0.022).
Conclusion: The DKD risk presented a threshold effect with the increase of TyG index, initially stable at a low level, and then gradually rising when the TyG index is above 9.35.
Keywords: diabetic kidney disease; insulin resistance; threshold effect; triglyceride glucose index; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Chen, Sun and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Associations between cardiometabolic indices and the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Apr 25;23(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02228-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38664793 Free PMC article.
-
Non-linear association of triglyceride-glucose index with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in T2DM patients with diabetic kidney disease: NHANES 2001-2018 retrospective cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Aug 17;23(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02249-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39154178 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the triglyceride glucose index, triglyceride-glucose body mass index and diabetic kidney disease in adults with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 24;11:1328601. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1328601. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38721354 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Diabetic Retinopathy: A Meta-Analysis.Horm Metab Res. 2024 Nov;56(11):785-794. doi: 10.1055/a-2279-7112. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Horm Metab Res. 2024. PMID: 38670124
-
The role of the triglyceride-glucose index as a biomarker of cardio-metabolic syndromes.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Dec 23;23(1):416. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02412-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39716258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Association Between Triglyceride Glucose-Body Mass Index and Kidney Impairment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Sep 16;17:3447-3453. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S477836. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39309307 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific and metabolic subgroup heterogeneity in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol associations with diabetic kidney disease risk: a retrospective cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Jun 7;24(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02632-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40483478 Free PMC article.
-
The association of triglyceride-glucose index and combined obesity indicators with chest pain and risk of cardiovascular disease in American population with pre-diabetes or diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 6;15:1471535. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1471535. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39309107 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index in predicting the risk of new-onset diabetes in the general population aged 45 years and older: a national prospective cohort study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Jan 26;25(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01848-w. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 39865224 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the C-reactive protein-triglyceride glucose index in predicting the risk of new-onset diabetes in the general population aged 45 years and older: a national prospective cohort study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 May 9;25(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01947-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40346472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen L, Hu Y, Ma Y, Wang H. Non-linear association of fasting C-peptide and uric acid levels with renal dysfunction based on restricted cubic spline in patients with type 2 diabetes: A real-world study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) (2023) 14:1157123. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1157123 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Sá JR, Rangel EB, Canani LH, Bauer AC, Escott GM, Zelmanovitz T, et al. . The 2021–2022 position of Brazilian Diabetes Society on diabetic kidney disease (DKD) management: an evidence-based guideline to clinical practice. Screening and treatment of hyperglycemia, arterial hypertension, and dyslipidemia in the patient with DKD. Diabetol Metab Syndr (2022) 14:81. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00843-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinese Diabetes Society. National Office of Basic Public Health Service Program for Primary Diabetes Care . [National technical guidelines for the prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease in primary care (2023)]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi (2023) 62:1394–405. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20231017-00223 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

