Hypoxic Preconditioning Promotes Survival of Human Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell
- PMID: 38938689
- PMCID: PMC11208860
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.55351.4
Hypoxic Preconditioning Promotes Survival of Human Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell
Abstract
Background: Contributing factors for improved survival of human adipocytes mesenchymal stem cells (h-AMSCs) cultured through hypoxia preconditioning, in example apoptosis inhibition involving BCL2 and HSP27 expression, trigger signal expression (VEGF), SCF expression, OCT-4 expression, and CD44+ expression. The objective if this study was to explain the mechanism and role of hypoxic preconditioning and the optimal duration of hypoxic preconditioning exposure to improve survival of h-AMSCs. Methods: An experimental laboratory explorative study ( in vitro) with hypoxic preconditioning in h-AMSCs cultures. This research was conducted through four stages. First, isolation of h-AMSCs culture from adipose tissue of patients. Second, the characterization of h-AMSCs from adipose tissue by phenotype (flowcytometry) through CD44+, CD90+ and CD45-expression before being pre-conditioned for hypoxic treatment. Third, the hypoxic preconditioning in h-AMSCs culture ( in vitro) was performed with an oxygen concentration of 1% for 24, 48 and 72 hours. Fourth, observation of survival from h-AMSCs culture was tested on the role of CD44+, VEGF, SCF, OCT-4, BCL2, HSP27 with Flowcytometry and apoptotic inhibition by Tunnel Assay method. Results: The result of regression test showed that time difference had an effect on VEGF expression ( p<0.001; β=-0.482) and hypoxia condition also influenced VEGF expression ( p<0.001; β=0.774). The result of path analysis showed that SCF had effect on OCT-4 expression ( p<0.001; β=0.985). The regression test results showed that time effects on HSP27 expression ( p<0.001; β=0.398) and hypoxia precondition also affects HSP27 expression ( p<0.001; β=0.847). Pathway analysis showed that BCL2 expression inhibited apoptosis ( p=0.030; β=-0.442) and HSP27 expression also inhibited apoptosis ( p<0,001; β=-0.487). Conclusion: Hypoxic preconditioning of h-AMSC culture has proven to increase the expression of VEGF, SCF, OCT-4, and BCL2 and HSP27. This study demonstrated and explained the existence of a new mechanism of increased h-AMSC survival in cultures with hypoxic preconditioning (O2 1%) via VEGF, SCF, OCT-4, BCL2, and HSP 27.
Keywords: BCL-2; HSP27; SCF; VEGF expression; apoptosis; h-AMSCs.
Copyright: © 2024 Suryawan IGR et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
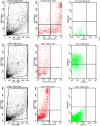
- A.
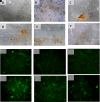
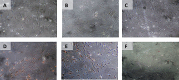
Phenotype expression of CD44+ was carried out by the flowcytometric method.
- B.
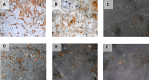
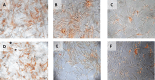
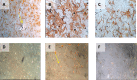
Immuno-cytochemical expression of VEGF.
- C.
Immunocytochemical expression of SCF from h-AMSCs culture.
- D.
Phenotype of OCT-4 expression (Immunocytochemistry and Immunofluorescence).


References
-
- Stępniewski J, Tomczyk M, Andrysiak K, et al. : Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes, in Contrast to Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Cells, Efficiently Improve Heart Function in Murine Model of Myocardial Infarction. Biomedicines. 2020;8(12):1–21. 10.3390/biomedicines8120578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

