Nanomedicine strategies for central nervous system (CNS) diseases
- PMID: 38938851
- PMCID: PMC11210682
- DOI: 10.3389/fbiom.2023.1215384
Nanomedicine strategies for central nervous system (CNS) diseases
Abstract
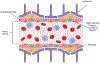
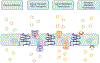
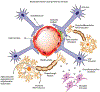
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a crucial part of brain anatomy as it is a specialized, protective barrier that ensures proper nutrient transport to the brain, ultimately leading to regulating proper brain function. However, it presents a major challenge in delivering pharmaceuticals to treat central nervous system (CNS) diseases due to this selectivity. A variety of different vehicles have been designed to deliver drugs across this barrier to treat neurodegenerative diseases, greatly impacting the patient's quality of life. The two main types of vehicles used to cross the BBB are polymers and liposomes, which both encapsulate pharmaceuticals to allow them to transcytose the cells of the BBB. For Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and glioblastoma brain cancer, there are a variety of different nanoparticle treatments in development that increase the bioavailability and targeting ability of existing drugs or new drug targets to decrease symptoms of these diseases. Through these systems, nanomedicine offers a new way to target specific tissues, especially for the CNS, and treat diseases without the systemic toxicity that often comes with medications used currently.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; Parkinson’s; blood-brain barrier; cancer; central nervous system disease; glioblastoma; multiple sclerosis; nanomedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest YC is a co-founder of Eascra Biotech, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author YC declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures



References
-
- alz (2023). Alzheimer’s facts and figures report | Alzheimer’s association. Available from: https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/facts-figures. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
