Coronary Plaque in People With HIV vs Non-HIV Asymptomatic Community and Symptomatic Higher-Risk Populations
- PMID: 38938873
- PMCID: PMC11198107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2024.100968
Coronary Plaque in People With HIV vs Non-HIV Asymptomatic Community and Symptomatic Higher-Risk Populations
Abstract
Background: People with HIV (PWH) have a high burden of coronary plaques; however, the comparison to people without known HIV (PwoH) needs clarification.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine coronary plaque burden/phenotype in PWH vs PwoH.
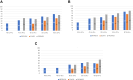
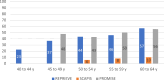
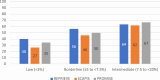
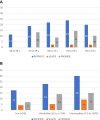
Methods: Nonstatin using participants from 3 contemporary populations without known coronary plaques with coronary CT were compared: the REPRIEVE (Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV) studying PWH without cardiovascular symptoms at low-to-moderate risk (n = 755); the SCAPIS (Swedish Cardiopulmonary Bioimage Study) of asymptomatic community PwoH at low-to-intermediate cardiovascular risk (n = 23,558); and the PROMISE (Prospective Multicenter Imaging Study for Evaluation of Chest Pain) of stable chest pain PwoH (n = 2,291). The coronary plaque prevalence on coronary CT was compared, and comparisons were stratified by 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk, age, and coronary artery calcium (CAC) presence.
Results: Compared to SCAPIS and PROMISE PwoH, REPRIEVE PWH were younger (50.8 ± 5.8 vs 57.3 ± 4.3 and 60.0 ± 8.0 years; P < 0.001) and had lower ASCVD risk (5.0% ± 3.2% vs 6.0% ± 5.3% and 13.5% ± 11.0%; P < 0.001). More PWH had plaque compared to the asymptomatic cohort (48.5% vs 40.3%; P < 0.001). When stratified by ASCVD risk, PWH had more plaque compared to SCAPIS and a similar prevalence of plaque compared to PROMISE. CAC = 0 was more prevalent in PWH (REPRIEVE 65.2%; SCAPIS 61.6%; PROMISE 49.6%); among CAC = 0, plaque was more prevalent in PWH compared to the PwoH cohorts (REPRIEVE 20.8%; SCAPIS 5.4%; PROMISE 12.3%, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Asymptomatic PWH in REPRIEVE had more plaque than asymptomatic PwoH in SCAPIS but had similar prevalence to a higher-risk stable chest pain cohort in PROMISE. In PWH, CAC = 0 does not reliably exclude plaque.
Keywords: asymptomatic community cohort; cardiovascular disease; coronary CT angiography; coronary plaque; people with HIV; stable chest pain.
Conflict of interest statement
10.13039/100000002This paper received NIH grants U01HL123336 to the REPRIEVE Clinical Coordinating Center and U01HL123339 to the REPRIEVE Data Coordinating Center, as well as funding from Kowa Pharmaceuticals, Gilead Sciences, and ViiV Healthcare. The 10.13039/100000060National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) supported this study through grants UM1 AI068636, which supports the AIDS Clinical Trials Group (ACTG) Leadership and Operations Center, and UM1 AI106701, which supports the ACTG Laboratory Center. The PROMISE trial was supported by the 10.13039/100000050National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (R01HL098237, R01HL098236, R01HL98305, and R01HL098235). The SCAPIS trial received funding from the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, Swedish Research Council and Vinnova (Sweden’s Innovation Agency), University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council, Linköping University and University Hospital, Lund University and Skåne University Hospital, Umeå University and University Hospital, and Uppsala University and University Hospital. The content of this manuscript is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily reflect the views of any of the funding agencies. Dr Lu has received funding to his institution from Kowa, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Johnson & Johnson Innovation, Ionis, and the American Heart Association unrelated to this research. Dr Taron has received funding by Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) (TA 1438/1-2); is on Speakers Bureau for Siemens Healthcare GmbH and Bayer AG; and has received consulting fees from Universimed Cross Media Content GmbH and Core Lab Black Forrest GmbH, unrelated to this work. Dr Foldyna has received funding to his institution from AstraZeneca/MedImmune, MedTrace, and Eli Lilly unrelated to this research. Dr Currier served as an advisor to Merck. Dr Elvstam has received grants to his institution from Pfizer; and has received honoraria as a speaker from Gilead Sciences, unrelated to this research. Dr Dubé has received funding to his institution from Gilead Sciences unrelated to this research. Dr Fichtenbaum has received funding to the institution from ViiV Healthcare, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Cytodyn, and Moderna unrelated to this work and serves on the advisory board for ViiV Healthcare. Dr Malvestutto has received funding to his institution from Lilly; and has received consulting fees from Viiv Healthcare and Gilead Sciences unrelated to this work. Dr Zanni reports being PI on research grants from the NIH (NHLBI and NIAID) and Gilead Sciences to her institution. Dr Ribaudo has received grants from Kowa Pharmaceuticals during the conduct of the study, as well as grants from NIH/NIAID, NIH/NHLBI, NIH/NIDDK, and NIH/NIA, outside the submitted work. Dr Grinspoon reports being a part of the Scientific Advisory Board for Marathon Asset Management and consultant Theratechnologies is unrelated to this report; research funds come from Gilead, Viiv, and Kowa through his institution. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Global HIV & AIDS statistics — 2020 fact sheet. https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 HL164285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069456/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI157882/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069412/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123336/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HL164284/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

