Coronary Artery Occlusion Detection Using 3-Lead ECG System Suitable for Credit Card-Size Personal Device Integration
- PMID: 38939446
- PMCID: PMC11198085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2023.100454
Coronary Artery Occlusion Detection Using 3-Lead ECG System Suitable for Credit Card-Size Personal Device Integration
Abstract
Background: Early coronary occlusion detection by portable personal device with limited number of electrocardiographic (ECG) leads might shorten symptom-to-balloon time in acute coronary syndromes.
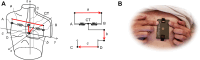
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to compare the accuracy of coronary occlusion detection using vectorcardgiographic analysis of a near-orthogonal 3-lead ECG configuration suitable for credit card-size personal device integration with automated and human 12 lead ECG interpretation.
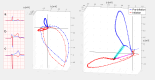
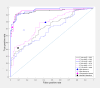
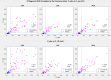
Methods: The 12-lead ECGs with 3 additional leads ("abc") using 2 arm and 2 left parasternal electrodes were recorded in 66 patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention prior to ("baseline", n = 66), immediately before ("preinflation", n = 66), and after 90-second balloon coronary occlusion ("inflation", n = 120). Performance of computer-measured ST-segment shift on vectorcardgiographic loops constructed from "abc" and 12 leads, standard 12-lead ECG, and consensus human interpretation in coronary occlusion detection were compared in "comparative" and "spot" modes (with/without reference to "baseline") using areas under ROC curves (AUC), reliability, and sensitivity/specificity analysis.
Results: Comparative "abc"-derived ST-segment shift was similar to two 12-lead methods (vector/traditional) in detecting balloon coronary occlusion (AUC = 0.95, 0.96, and 0.97, respectively, P = NS). Spot "abc" and 12-lead measurements (AUC = 0.72, 0.77, 0.68, respectively, P = NS) demonstrated poorer performance (P < 0.01 vs comparative measurements). Reliability analysis demonstrated comparative automated measurements in "good" agreement with reference (preinflation/inflation), while comparative human interpretation was in "moderate" range. Spot automated and human reading showed "poor" agreement.
Conclusions: Vectorcardiographic ST-segment analysis using baseline comparison of 3-lead ECG system suitable for credit card-size personal device integration is similar to established 12-lead ECG methods in detecting balloon coronary occlusion.
Keywords: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; acute coronary syndrome; electrocardiography; myocardial ischemia; vectorcardiography.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs Shvilkin, Vukčević, Vukajlović, Bojović, Hadžievski, and Atanasoskiare are stockholders of HeartBeam, Inc. Drs Miletić, Zimetbaum, and Gibson have received consulting fees from HeartBeam, Inc. Dr Vajdic is CEO, HeartBeam, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- De Luca G., Suryapranata H., Zijlstra F., et al. Symptom-onset-to-balloon time and mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction treated by primary angioplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:991–997. - PubMed
-
- Gibson C.M. Time is myocardium and time is outcomes. Circulation. 2001;104:2632–2634. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg R.J., Spencer F.A., Fox K.A., et al. Prehospital delay in patients with acute coronary syndromes (from the Global Registry of acute coronary events [GRACE]) Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:598–603. - PubMed
-
- Marcolino M.S., Maia L.M., Oliveira J.A.Q., et al. Impact of telemedicine interventions on mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart. 2019;105(19):1479–1486. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

