Unpacking extracellular vesicles: RNA cargo loading and function
- PMID: 38939528
- PMCID: PMC11080855
- DOI: 10.1002/jex2.40
Unpacking extracellular vesicles: RNA cargo loading and function
Abstract
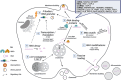
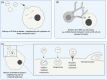
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are a heterogeneous group of membrane-enclosed structures produced by prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. EVs carry a range of biological cargoes, including RNA, protein, and lipids, which may have both metabolic significance and signalling potential. EV release has been suggested to play a critical role in maintaining intracellular homeostasis by eliminating unnecessary biological material from EV producing cells, and as a delivery system to enable cellular communication between both neighbouring and distant cells without physical contact. In this review, we give an overview of what is known about the relative enrichment of the different types of RNA that have been associated with EVs in the most recent research efforts. We then examine the selective and non-selective incorporation of these different RNA biotypes into EVs, the molecular systems of RNA sorting into EVs that have been elucidated so far, and the role of this process in EV-producing cells. Finally, we also discuss the model systems providing evidence for EV-mediated delivery of RNA to recipient cells, and the implications of this evidence for the relevance of this RNA delivery process in both physiological and pathological scenarios.
Keywords: EVs; RBPs; RNA; RNA loading; RNA‐binding proteins; delivery; extracellular vesicles; intercellular communication; loading; motifs; zipcodes.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Biology published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abels, E. R. , Maas, S. L. N. , Nieland, L. , Wei, Z. , Cheah, P. S. , Tai, E. , Kolsteeg, C.‐J. , Dusoswa, S. A. , Ting, D. T. , Hickman, S. , El Khoury, J. , Krichevsky, A. M. , Broekman, M. L. D. , & Breakefield, X. O. (2019). Glioblastoma‐associated microglia reprogramming is mediated by functional transfer of extracellular miR‐21. Cell Reports, 28, 3105–3119.e7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albanese, M. , Chen, Y‐F. A. , Hüls, C. , Gärtner, K. , Tagawa, T. , Mejias‐Perez, E. , Keppler, O. T. , Göbel, C. , Zeidler, R. , Shein, M. , Schütz, A. K. , & Hammerschmidt, W. (2021). MicroRNAs are minor constituents of extracellular vesicles that are rarely delivered to target cells. Plos Genetics, 17, e1009951. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arroyo, J. D. , Chevillet, J. R. , Kroh, E. M. , Ruf, I. K. , Pritchard, C. C. , Gibson, D. F. , Mitchell, P. S. , Bennett, C. F. , Pogosova‐Agadjanyan, E. L. , Stirewalt, D. L. , Tait, J. F. , & Tewari, M. (2011). Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108, 5003–5008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baglio, S. R. , Rooijers, K. , Koppers‐Lalic, D. , Verweij, F. J. , Pérez Lanzón, M. , Zini, N. , Naaijkens, B. , Perut, F. , Niessen, H. W. M. , Baldini, N. , & Pegtel, D. M. (2015). Human bone marrow‐ and adipose‐mesenchymal stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in distinctive miRNA and tRNA species. Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 6, 127. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
