Capturing the art and science of dentistry in a lens: Digital dental photography
- PMID: 38939543
- PMCID: PMC11205163
- DOI: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_12_24
Capturing the art and science of dentistry in a lens: Digital dental photography
Abstract
Dental photography is now an excellent tool that plays a crucial role in dentistry as it helps in documenting and analyzing the oral conditions of patients. Photography provides a visual representation of the teeth, gums, and other oral structures, which aids in diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring the progress of treatment. Therefore, it is essential for dental professionals to understand the importance of dental photography and incorporate photography it into regular practice. The purpose of this paper is to provide emphasis and elucidate the path of dental photography easier for dental student and practitioner.
Keywords: Dental; esthetic; extraoral; intraoral; photography.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
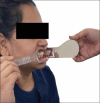
Figures










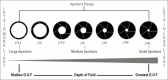


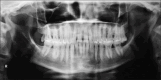

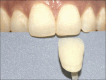
References
-
- Patel C. An overview on dental photography. Int J Dent Health Sci. 2016;3:581–9.
-
- Wander P. A history of Dental Photography. Dental Historian. 2017;62:64–9.
-
- Dragan M, Lidija M. Importance of digital dental photography in the practice of dentistry. Acta Fac Med Naissensis. 2010;27:75–9.
-
- Christensen GJ. Important clinical uses for digital photography. J Am Dent Assoc. 2005;136:77–9. - PubMed
-
- Antar F, Zebouni E. Comparative review of DSLR cameras and smartphones in dental photography: Indications and limitations. Int Arab J Dent. 2018;9:107–115.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
