Can Artificial Intelligence Enhance Syncope Management?: A JACC: Advances Multidisciplinary Collaborative Statement
- PMID: 38939607
- PMCID: PMC11198330
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2023.100323
Can Artificial Intelligence Enhance Syncope Management?: A JACC: Advances Multidisciplinary Collaborative Statement
Abstract
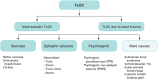
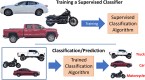
Syncope, a form of transient loss of consciousness, remains a complex medical condition for which adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including death, are of major concern but rarely occur. Current risk stratification algorithms have not completely delineated which patients benefit from hospitalization and specific interventions. Patients are often admitted unnecessarily and at high cost. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning may help define the transient loss of consciousness event, diagnose the cause, assess short- and long-term risks, predict recurrence, and determine need for hospitalization and therapeutic intervention; however, several challenges remain, including medicolegal and ethical concerns. This collaborative statement, from a multidisciplinary group of clinicians, investigators, and scientists, focuses on the potential role of AI in syncope management with a goal to inspire creation of AI-derived clinical decision support tools that may improve patient outcomes, streamline diagnostics, and reduce health-care costs.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; emergency department; machine learning; syncope; transient loss of consciousness.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was funded by the Iowa Initiative for Artificial Intelligence (IIAI), Carver College of Medicine Office of Research, University of Iowa. Dr Olshansky is on the Data and Safety Monitoring Board of AstraZeneca. Dr Sonka is an inventor and has patents and patent applications in computer vision and medical image analysis; and is a cofounder of Medical Imaging Applications, LLC, Coralville, Iowa, USA and VIDA Diagnostics, Inc, Coralville, Iowa, USA. Dr Venkatesh Thiruganasambandamoorthy is supported through a Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation Mid-Career Clinical Researcher award and University of Ottawa Tier-1 Clinical Research Chair in Cardiovascular Emergencies award. Dr Thiruganasambandamoorthy has received peer-reviewed grant funds for studies from the following governmental or non-profit agencies: the 10.13039/501100000241Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation—Ontario, Canada, 10.13039/501100000024Canadian Institutes of Health Research, 10.13039/100004411Heart and Stroke Foundation Canada, and the Cardiac Arrhythmia Network of Canada as part of the Networks of Centres of Excellence (NCE; and is a consultant for the NIH funded Practical Approaches to Care in Emergency Syncope (PACES) study. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Matthews I.G., Lawson J., Parry S.W., Davison J. A survey of the management of transient loss of consciousness in the emergency department. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2014;44:10–13. - PubMed
-
- Brignole M., Moya A., de Lange F.J., et al. 2018 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:1883–1948. - PubMed
-
- Grubb B.P. In: Chapter 1. Syncope: Overview and Approach to Management. 2nd ed. Grubb B.P., Olshansky B., editors. Blackwell Futura Publishing Company; 2005. Syncope: mechanisms and management; pp. 1–49.
-
- Reed M.J. Approach to syncope in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2019;36:108–116. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

