Optimal isolation of extracellular vesicles from pleural fluid and profiling of their microRNA cargo
- PMID: 38939736
- PMCID: PMC11080846
- DOI: 10.1002/jex2.119
Optimal isolation of extracellular vesicles from pleural fluid and profiling of their microRNA cargo
Abstract
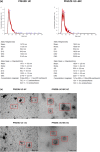
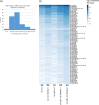
Pleural effusion occurs in both benign and malignant pleural disease. In malignant pleural effusions, the diagnostic accuracy and sensitivity of pleural fluid cytology is less than perfect, particularly for the diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma, but also in some cases for the diagnosis of metastatic pleural malignancy with primary cancer in the lung, breast or other sites. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) carry an enriched cargo of microRNAs (miRNAs) which are selectively packaged and differentially expressed in pleural disease states. To investigate the diagnostic potential of miRNA cargo in pleural fluid extracellular vesicles (PFEVs), we evaluated methods for isolating the extracellular vesicle (EV) fraction including combinations of ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) and ultrafiltration (10 kDa filter unit). PFEVs were characterized by total and EV-associated protein, nanoparticle tracking analysis and visualisation by transmission electron microscopy. miRNA expression was analyzed by Nanostring nCounter® in separate EV fractions isolated from pleural fluid with or without additional RNA purification by ultrafiltration (3 kDa filter unit). Optimal PFEV yield, purity and miRNA expression were observed when PFEV were isolated from a larger volume of pleural fluid processed through combined ultracentrifugation and SEC techniques. Purification of total RNA by ultrafiltration further enhanced the detectability of PFEV miRNAs. This study demonstrates the feasibility of isolating PFEVs, and the potential to examine PFEV miRNA cargo using Nanostring technology to discover disease biomarkers.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles (EVs); microRNA (miRNAs); microvesicles; nanostring; pleural fluid.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Biology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Potential utility of miRNAs derived from pleural fluid extracellular vesicles to differentiate between benign and malignant pleural effusions.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 24;14(1):124-138. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-945. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39958230 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA in Malignant Pleural Effusion.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 19;13(11):2159. doi: 10.3390/genes13112159. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421832 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Utility of the Extracellular Vesicles Subpopulations Present in Pleural Effusion.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 29;11(11):1606. doi: 10.3390/biom11111606. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827604 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing microRNA-enriched extracellular vesicles for liquid biopsy.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Feb 21;11:1356780. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1356780. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38449696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A review.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020 Jun;150:102949. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.102949. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32330840 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid isolation of extracellular vesicles from stem cell conditioned medium using osmosis-driven filtration.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2025 Apr 3;26(1):2485668. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2025.2485668. eCollection 2025. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40241847 Free PMC article.
-
Potential utility of miRNAs derived from pleural fluid extracellular vesicles to differentiate between benign and malignant pleural effusions.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 24;14(1):124-138. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-945. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39958230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calin, G. A. , Ferracin, M. , Cimmino, A. , Di Leva, G. , Shimizu, M. , Wojcik, S. E. , Iorio, M. V. , Visone, R. , Sever, N. I. , Fabbri, M. , Iuliano, R. , Palumbo, T. , Pichiorri, F. , Roldo, C. , Garzon, R. , Sevignani, C. , Rassenti, L. , Alder, H. , Volinia, S. , … Croce, C. M. (2005). A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. The New England Journal of Medicine, 353(17), 1793–1801. - PubMed
-
- Cappellesso, R. , Galasso, M. , Nicolè, L. , Dabrilli, P. , Volinia, S. , & Fassina, A. (2017). miR‐130A as a diagnostic marker to differentiate malignant mesothelioma from lung adenocarcinoma in pleural effusion cytology. Cancer Cytopathology, 125(8), 635–643. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
