A learned score function improves the power of mass spectrometry database search
- PMID: 38940129
- PMCID: PMC11211853
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae218
A learned score function improves the power of mass spectrometry database search
Abstract
Motivation: One of the core problems in the analysis of protein tandem mass spectrometry data is the peptide assignment problem: determining, for each observed spectrum, the peptide sequence that was responsible for generating the spectrum. Two primary classes of methods are used to solve this problem: database search and de novo peptide sequencing. State-of-the-art methods for de novo sequencing use machine learning methods, whereas most database search engines use hand-designed score functions to evaluate the quality of a match between an observed spectrum and a candidate peptide from the database. We hypothesized that machine learning models for de novo sequencing implicitly learn a score function that captures the relationship between peptides and spectra, and thus may be re-purposed as a score function for database search. Because this score function is trained from massive amounts of mass spectrometry data, it could potentially outperform existing, hand-designed database search tools.
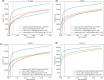
Results: To test this hypothesis, we re-engineered Casanovo, which has been shown to provide state-of-the-art de novo sequencing capabilities, to assign scores to given peptide-spectrum pairs. We then evaluated the statistical power of this Casanovo score function, Casanovo-DB, to detect peptides on a benchmark of three mass spectrometry runs from three different species. In addition, we show that re-scoring with the Percolator post-processor benefits Casanovo-DB more than other score functions, further increasing the number of detected peptides.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Bai W, Bilmes JA, Noble WS. Bipartite matching generalizations for peptide identification in tandem mass spectrometry. In: ACM Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology, and Health Informatics, Seattle, WA, New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery 2016, 327–36.
-
- Cox J, Neuhauser N, Michalski A. et al. Andromeda: a peptide search engine integrated into the MaxQuant environment. J Proteome Res 2011;10:1794–805. - PubMed
-
- Craig R, Beavis RC.. Tandem: matching proteins with tandem mass spectra. Bioinformatics 2004;20:1466–7. - PubMed
-
- Elias JE, Gygi SP.. Target-decoy search strategy for increased confidence in large-scale protein identifications by mass spectrometry. Nat Methods 2007;4:207–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

