Partial RNA design
- PMID: 38940170
- PMCID: PMC11256918
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae222
Partial RNA design
Abstract
Motivation: RNA design is a key technique to achieve new functionality in fields like synthetic biology or biotechnology. Computational tools could help to find such RNA sequences but they are often limited in their formulation of the search space.
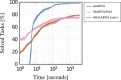
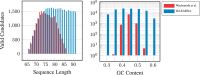
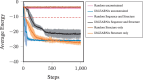
Results: In this work, we propose partial RNA design, a novel RNA design paradigm that addresses the limitations of current RNA design formulations. Partial RNA design describes the problem of designing RNAs from arbitrary RNA sequences and structure motifs with multiple design goals. By separating the design space from the objectives, our formulation enables the design of RNAs with variable lengths and desired properties, while still allowing precise control over sequence and structure constraints at individual positions. Based on this formulation, we introduce a new algorithm, libLEARNA, capable of efficiently solving different constraint RNA design tasks. A comprehensive analysis of various problems, including a realistic riboswitch design task, reveals the outstanding performance of libLEARNA and its robustness.
Availability and implementation: libLEARNA is open-source and publicly available at: https://github.com/automl/learna_tools.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advanced Design of Structural RNAs Using RNARedPrint.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2284:1-15. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1307-8_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33835434
-
RiboDiffusion: tertiary structure-based RNA inverse folding with generative diffusion models.Bioinformatics. 2024 Jun 28;40(Suppl 1):i347-i356. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae259. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38940178 Free PMC article.
-
RNAiFOLD: a constraint programming algorithm for RNA inverse folding and molecular design.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2013 Apr;11(2):1350001. doi: 10.1142/S0219720013500017. Epub 2013 Feb 6. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23600819
-
Design of RNAs: comparing programs for inverse RNA folding.Brief Bioinform. 2018 Mar 1;19(2):350-358. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw120. Brief Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 28049135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving methods for rational de novo design of functional RNA molecules.Methods. 2019 May 15;161:54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.04.022. Epub 2019 May 4. Methods. 2019. PMID: 31059832 Review.
Cited by
-
Secondary-Structure-Informed RNA Inverse Design via Relational Graph Neural Networks.Noncoding RNA. 2025 Feb 26;11(2):18. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11020018. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40126342 Free PMC article.
-
DRAG: design RNAs as hierarchical graphs with reinforcement learning.Brief Bioinform. 2025 Mar 4;26(2):bbaf106. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf106. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40079262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andronescu M, Fejes AP, Hutter F et al. A new algorithm for RNA secondary structure design. J Mol Biol 2004;336:607–24. - PubMed
-
- Busch A, Backofen R. Info-RNA—a fast approach to inverse RNA folding. Bioinformatics 2006;22:1823–31. - PubMed
-
- Devlin J, Chang M-W, Lee K, Toutanova K. . BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In: Burstein J, Doran C, Solorio T (eds.), Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Minneapolis, MN: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019, 4171–86.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

