Plasma amyloid beta X-42/X-40 ratio and cognitive decline in suspected early and preclinical Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38940303
- PMCID: PMC11350048
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13909
Plasma amyloid beta X-42/X-40 ratio and cognitive decline in suspected early and preclinical Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Blood-based biomarkers are a cost-effective and minimally invasive method for diagnosing the early and preclinical stages of amyloid positivity (AP). Our study aims to investigate our novel immunoprecipitation-immunoassay (IP-IA) as a test for predicting cognitive decline.
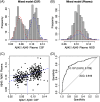
Methods: We measured levels of amyloid beta (Aβ)X-40 and AβX-42 in immunoprecipitated eluates from the DELCODE cohort. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves, regression analyses, and Cox proportional hazard regression models were constructed to predict AP by Aβ42/40 classification in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and conversion to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia.
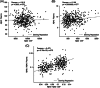
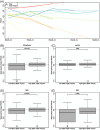
Results: We detected a significant correlation between AßX-42/X-40 in plasma and CSF (r = 0.473). Mixed-modeling analysis revealed a substantial prediction of AßX-42/X-40 with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.81 for AP (sensitivity: 0.79, specificity: 0.74, positive predictive value [PPV]: 0.71, negative predictive value [NPV]: 0.81). In addition, lower AβX-42/X-40 ratios were associated with negative PACC5 slopes, suggesting cognitive decline.
Discussion: Our results suggest that assessing the plasma AβX-42/X-40 ratio via our semiautomated IP-IA is a promising biomarker when examining patients with early or preclinical AD.
Highlights: New plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 measurement using immunoprecipitation-immunoassay Plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 associated with longitudinal cognitive decline Promising biomarker to detect subjective cognitive decline at-risk for brain amyloid positivity.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; MCI; amyloid beta; biomarker; dementia; plasma.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
J.V.: DFG/Clinician Scientist Kolleg (#413501650) and McLean Eric Dorris Memorial Fellowship. N.H.: DFG (530229798), Lilly AG travel support. S.T.: Advisory Board Memberships for Biogen, Eisai, Lilly; Member of the Independent Data Safety and Monitoring Board for ENVISION (Biogen). E.D.: Paid consultancy work and talks for Roche, Lilly, Eisai, Biogen, neotiv, and UCLC; Holds shares of neotiv. C.B.: Employee of MicroDiscovery GmbH. MicroDiscovery was paid by University Goettingen for supporting the statistical analysis. J.S.: Employee of MicroDiscovery GmbH. MicroDiscovery was paid by University Goettingen for supporting the statistical analysis. C.l.B.: received honoraria as a diagnostic consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim (last time: 10/2019); received honoraria for lectures from Roche (06/2021); received funding from the German Alzheimer Association (DAlzG; 2021‐2023). O.P.: Paid consultancy work and talks for Biogen, Eisai, Grifols, Lilly, Noselab, Prinnovation, Schwabe, and Roche. F.M.: Employee of ki:elements GmbH. J.W.: Paid consultancy and talks for Abbott, Actelion, Amgen, Beeijing Yibai Science and Technology Ltd., Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gloryren, Immungenetics, Janssen‐Cilag, Lilly, medUpdate GmbH, MSD Sharp & Dohme, Noselab, Pfizer, Roche, and Roboscreen; holds patents PCT/EP2011 001724 and PCT/EP 2015 052945. M.S., M.W., H.K., B.M., A.J.B., B.S., H.E., L.K., S.W., L.S.S., X.W., J.P., E.S., S.A., A.L., A.S., K.F., I.V., F.J., A.R., W.G., E.I., M.B., K.B., D.J., E.W., R.P., B.R., S.G., I.K., D.G., C.L., M.M., C.S., A.Sp., N.R.K., M.H., F.B., A.R., and M.S. did not report any disclosures. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures


References
-
- Collaborators G 2019 DF , Nichols E, Steinmetz JD, et al, Collaborators G 2019 DF . Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Heal. 2022;7:e105‐e125. doi:10.1016/s2468-2667(21)00249-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carrillo MC, Snyder H, Andrews JS, et al. NIA‐AA Revised Clinical Guidelines for Alzheimer's n.d. (accessed July 17, 2023). https://aaic.alz.org/nia‐aa.asp
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

