Preclinical evaluation of ELP-004 in mice
- PMID: 38940379
- PMCID: PMC11212004
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.1230
Preclinical evaluation of ELP-004 in mice
Abstract
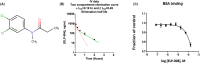
This study provides a detailed understanding of the preclinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism of ELP-004, an osteoclast inhibitor in development for the treatment of bone erosion. Current treatments for arthritis, including biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, are not well-tolerated in a substantial subset of arthritis patients and are expensive; therefore, new treatments are needed. Pharmacokinetic parameters of ELP-004 were tested with intravenous, oral, and subcutaneous administration and found to be rapidly absorbed and distributed. We found that ELP-004 was non-mutagenic, did not induce chromosome aberrations, non-cardiotoxic, and had minimal off-target effects. Using in vitro hepatic systems, we found that ELP-004 is primarily metabolized by CYP1A2 and CYP2B6 and predicted metabolic pathways were identified. Finally, we show that ELP-004 inhibits osteoclast differentiation without suppressing overall T-cell function. These preclinical data will inform future development of an oral compound as well as in vivo efficacy studies in mice.
Keywords: CYP450; metabolism; mice; osteoclast; pharmacokinetics; preclinical.
© 2024 The Author(s). Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
JBB is the President and Chief Science Officer of ExesaLibero Pharma, Inc. JBB, WJG, BCGS, HCB, and JS serve on the Scientific Advisory Board of ExesaLibero Pharma, Inc. Drs. JBB, JS, and HCB have a patent [US 10,682,320 B2] on methods for inhibiting osteoclast development which includes the use of ELP‐004. JLM is an employee of ExesaLibero Pharma, Inc. LJR, PMG, and MRW declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Choy E. Understanding the dynamics: pathways involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51(Suppl 5):v3‐v11. - PubMed
-
- Matcham F, Scott IC, Rayner L, et al. The impact of rheumatoid arthritis on quality‐of‐life assessed using the SF‐36: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;44(2):123‐130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

