The Dual Innervation of the Gluteus Maximus Associated with Other Anatomical Variations of the Gluteal Region
- PMID: 38940504
- PMCID: PMC11572275
- DOI: 10.4274/MMJ.galenos.2024.83652
The Dual Innervation of the Gluteus Maximus Associated with Other Anatomical Variations of the Gluteal Region
Abstract
The gluteus maximus (GM) is a big quadrilateral musculature that lines the rear portion of the pelvis. It is innervated by the inferior gluteal nerve. The sciatic nerve, inferior gluteal nerve, and posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh are branches of the sacral plexus. The superior and inferior gluteal arteries are the chief arterial supply to the gluteal region. In the present case, there was a dual innervation of the GM. The superior gluteal artery and the superior gluteal nerve was piercing the piriformis and the inferior gluteal artery was running between the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh and the inferior gluteal nerve. According to our literature review, anatomical studies in which this cadaveric procedure has been performed have not been previously reported. The anatomical variations of the gluteal region are important to surgeons, physicians, anatomists, and nurses.
Gluteus maksimus (GM) pelvisin arka kısmını kaplayan büyük bir dörtgen kas sistemidir. İnferior gluteal sinir tarafından innerve edilir. Siyatik sinir, inferior gluteal sinir ve uyluğun posterior kutanöz siniri sakral pleksusun dallarıdır. Süperior ve inferior gluteal arterler gluteal bölgenin başlıca arteriyel beslenmesidir. Mevcut olguda, GM ve superior gluteal arterin ikili bir innervasyonu vardı. Superior gluteal sinir piriformisi delmekte ve inferior gluteal arter uyluğun posterior kutanöz siniri ile inferior gluteal sinir arasında seyretmekteydi. Literatür taramamıza göre, bu kadavra prosedürünün uygulandığı anatomik çalışmalar daha önce bildirilmemiştir. Gluteal bölgenin anatomik varyasyonları cerrahlar, hekimler, anatomistler ve hemşireler için önemlidir.
Keywords: Gluteus maximus; cadaver; dual innervation; piriformis; sciatic nerve.
Copyright© 2024 The Author. Published by Galenos Publishing House on behalf of Istanbul Medeniyet University Faculty of Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
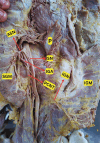
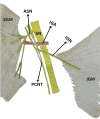
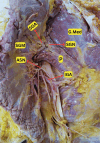
Similar articles
-
The inferior gluteal nerve often has a cutaneous branch: A discovery with application to hip surgery and targeting gluteal pain syndromes.Clin Anat. 2018 Sep;31(6):937-941. doi: 10.1002/ca.23232. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Clin Anat. 2018. PMID: 30335198
-
Inferior Gluteal Nerve Injury.2023 Sep 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Sep 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32644392 Free Books & Documents.
-
Report of a Novel Bilateral Variation of Sciatic and Inferior Gluteal Nerve: A Case Study.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2021 May-Jun;12(3):421-426. doi: 10.32598/bcn.2021.1900.1. Epub 2021 May 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34917300 Free PMC article.
-
[Piriformis muscle syndrome: etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and therapy].Lijec Vjesn. 2013 Jan-Feb;135(1-2):33-40. Lijec Vjesn. 2013. PMID: 23607175 Review. Croatian.
-
Clinical anatomy of the inferior gluteal nerve - systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Anat. 2025 Jun;260:152661. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2025.152661. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Ann Anat. 2025. PMID: 40220798
References
-
- Standring S. Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 41st edition. New York: Elsevier Limited, 2016.
-
- Quiñones-Rodríguez J, Camacho-Quiñones A, Cárdenas-Suárez NY, Ramírez N. Dual Innervation to the Gluteus Maximus: A Case Report with Clinical Implications. J Clin of Diagn Res. 2022;16:AD01–3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
