Novel Perspective on the Plasticity of Taste Perception: Is Food- and Exercise-Induced Inflammation Associated with Sweet Taste Sensitivity and Preference?
- PMID: 38941285
- PMCID: PMC11247480
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09028
Novel Perspective on the Plasticity of Taste Perception: Is Food- and Exercise-Induced Inflammation Associated with Sweet Taste Sensitivity and Preference?
Abstract
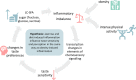
Obesity-related inflammation has been linked to decreased taste sensitivity and changes in the transcriptome of the taste apparatus. Increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines can also be found to be food-associated in individuals who consume high amounts of long-chain saturated fatty acids and sucrose independent of the body composition or individuals who exercise intensively. Previous research suggests a link between taste sensitivity and food choices. However, the interplay between food- or exercise-induced low-grade inflammation, taste perception, and food choices remains unaddressed. Understanding this relationship could provide an unnoticed explanation for interindividual differences in taste perception that influences dietary habits.
Keywords: food choices; inflammation; physical activity; taste perception; taste preferences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Taste preferences in association with dietary habits and weight status in European children: results from the IDEFICS study.Int J Obes (Lond). 2012 Jan;36(1):27-34. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2011.164. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012. PMID: 21844876
-
Sweet and Umami Taste Perception Differs with Habitual Exercise in Males.Nutrients. 2019 Jan 12;11(1):155. doi: 10.3390/nu11010155. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30642050 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal sweet taste dominance according to adult body mass index classification.J Food Sci. 2023 May;88(5):2191-2202. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16556. Epub 2023 Apr 5. J Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37020388
-
Genetic variation in taste and its influence on food selection.OMICS. 2009 Feb;13(1):69-80. doi: 10.1089/omi.2008.0031. OMICS. 2009. PMID: 18687042 Review.
-
Effect of Physical Exercise on Taste Perceptions: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 9;12(9):2741. doi: 10.3390/nu12092741. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32916826 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

