Acupuncture combined with mirror therapy for post-stroke dyskinesia: A meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 38941386
- PMCID: PMC11466092
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038733
Acupuncture combined with mirror therapy for post-stroke dyskinesia: A meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Background: Dyskinesia is one of the most common complications of stroke. Acupuncture therapy (AT) and mirror therapy (MT) are promising rehabilitation measures for the treatment of post-stroke dyskinesia. Although some studies suggested that AT and MT are effective and safe for dyskinesia, the effects, and safety remain uncertain due to lacking strong evidence. The purpose of this study is to investigate the efficacy and safety of AT combined with MT in the treatment of post-stroke dyskinesia.
Methods: We searched the following databases: PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Medline, China Knowledge Network, WANFANG, and China Biomedical Literature Database, from inception to 1 January 2023 to identify eligible studies. Total effective rate, the Fugl-Meyer assessment scale (FMA) upper and lower limb scores, modified Barthel index scores, Berg balance scale, modified Ashworth scale, and adverse reactions were adopted as outcome indicators. The Grading of Recommendations Assessment Development and Evaluation system was used by 2 independent reviewers to assess the quality of evidence for the outcome indicators included in the study. The statistical analysis was conducted by RevMan V.5.4 software.
Results: A total of 24 randomized controlled studies included 2133 patients with post-stroke dyskinesia were included. The total effective rate of AT combined with MT was more advantageous in the treatment of post-stroke dyskinesia (relative risk = 1.31, 95% confidence interval [CI] [1.22-1.42], Z = 6.96, P < .0001). AT combined with MT was more advantageous for FMA upper limb score (mean difference [MD] = 6.67, 95% CI [5.21-8.13], Z = 8.97, P < .00001) and FMA lower limb score (MD = 3.72, 95% CI [2.81-4.63], Z = 7.98, P < .00001). Meta-analysis showed that AT combined with MT for post-stroke dyskinesia had a more advantageous modified Barthel index score (MD = 9.51, 95% CI [7.44-11.58], Z = 9.01, P < .00001).
Conclusion: AT combined with MT is effective in improving motor function and daily living ability of patients, especially in improving muscle spasms. However, these results should be regarded with caution given the low quality of evidence for the evaluation results.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


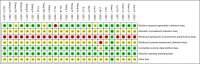









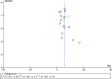
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of acupuncture combined with mirror therapy in the treatment of post-stroke limb movement disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Front Rehabil Sci. 2024 Nov 7;5:1464502. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2024.1464502. eCollection 2024. Front Rehabil Sci. 2024. PMID: 39575345 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of acupuncture on lower limb motor dysfunction following stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.PLoS One. 2025 May 7;20(5):e0312918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312918. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40333934 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of eye-acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training for poststroke dyskinesia: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Mar 12;100(10):e25036. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025036. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33725887 Free PMC article.
-
Scalp acupuncture for post-stroke spastic hemiparesis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Mar 1;103(9):e37167. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037167. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38428878 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of acupuncture in the treatment of limb dyskinesia after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Nov;27(22):10985-10993. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202311_34467. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38039029
Cited by
-
Efficacy of acupuncture combined with mirror therapy in the treatment of post-stroke limb movement disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Front Rehabil Sci. 2024 Nov 7;5:1464502. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2024.1464502. eCollection 2024. Front Rehabil Sci. 2024. PMID: 39575345 Free PMC article.
-
Multidimensional evaluation of the clinical efficacy and potential mechanisms of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training in the treatment of stroke: a study based on multiple evaluation indicators.Front Neurol. 2025 May 21;16:1573073. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1573073. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40470494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese multidisciplinary expert consensus on stroke disease monitoring. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;101:317–26.
-
- Cramer SC, Chopp M. Recovery recapitulates ontogeny. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:265–71. - PubMed
-
- Su DY. Meta-analysis of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of post-stroke dyskinesia. Chongqing, China: Chongqing Medical University; 2022.
-
- Ford B, Peela S, Roberts C. Secondary prevention of ischemic stroke: updated guidelines from AHA/ASA. Am Fam Physician. 2022;105:99–102. - PubMed
-
- Morkisch N, Thieme H, Dohle C. How to perform mirror therapy after stroke? Evidence from a meta-analysis. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2019;37:421–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

