Advancements in the investigation of chemical components and pharmacological properties of Codonopsis: A review
- PMID: 38941387
- PMCID: PMC11466214
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038632
Advancements in the investigation of chemical components and pharmacological properties of Codonopsis: A review
Abstract
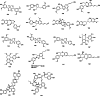
Species of the genus Codonopsis (Campanulaceae) have a long history of application, acclaimed for its edible and therapeutic attributes. Scholarly inquiries into Codonopsis span botany, phytochemistry, quality assurance, pharmacodynamics, and toxicity, revealing a rich and comprehensive body of knowledge. This study synthesizes information from esteemed scientific databases like SciFinder, PubMed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and Chinese herbal classics to create a thorough scientific conceptual and theoretical framework for Codonopsis research. In this article, the phytochemical composition includes saccharides, polyacetylenes, polyenes, flavonoids, alkaloids, lignans, terpenoids, and organic acids was summarized. To date, over 350 monomeric compounds have been isolated and identified from Codonopsis, with recent studies primarily focusing on polysaccharides, aromatic derivatives, lignans, and polyacetylenes. Codonopsis exhibits broad pharmacological activities across various systems, including immune, blood, cardiovascular, central nervous, and digestive systems, with no significant toxicity or adverse effects reported. The existing research, focusing on various extracts and active parts without identifying specific active molecules, complicates the understanding of the mechanisms of action. There is an urgent need to advance research on the chemical composition and pharmacological effects to fully elucidate its pharmacodynamic properties and the basis of its material composition. Such efforts are crucial for the rational development, utilization, and clinical application of this herb.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Codonopsis: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jun 12;219:50-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.02.039. Epub 2018 Feb 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29501674 Review.
-
A review of the botany, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, analysis method and quality control, processing methods, pharmacological effects, pharmacokinetics and toxicity of codonopsis radix.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1162036. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1162036. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37089919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research progress of Codonopsis Radix and prediction of its Q-markers].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Apr;48(8):2020-2040. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20221231.202. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37282892 Chinese.
-
Recent bioanalytical methods for the isolation of bioactive natural products from genus Codonopsis.Phytochem Anal. 2023 Jul;34(5):491-506. doi: 10.1002/pca.3253. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Phytochem Anal. 2023. PMID: 37316180 Review.
-
The genus Codonopsis (Campanulaceae): a review of phytochemistry, bioactivity and quality control.J Nat Med. 2015 Jan;69(1):1-21. doi: 10.1007/s11418-014-0861-9. Epub 2014 Aug 7. J Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25099952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prediction of Chemical Composition and Sensory Information of Codonopsis Radix Based on Electronic Nose.Molecules. 2025 Mar 3;30(5):1146. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051146. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076370 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of traditional Chinese medicine in cancer treatment via immune system modulation (2015-2025).Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1581885. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1581885. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406101 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement on mitochondrial energy metabolism of Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf. polysaccharide.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 30;16:1545356. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1545356. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40520160 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on the improvement of agronomic traits and key enzyme-coding genes related to polysaccharide biosynthesis in Codonopsis pilosula.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 3;20(6):e0319989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319989. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40460104 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptogens in Long-Lasting Brain Fatigue: An Insight from Systems Biology and Network Pharmacology.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 15;18(2):261. doi: 10.3390/ph18020261. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hong DY. A Monograph of Codonopsis and Allied Genera (Campanulaceae). Academic Press, Massachusetts, 2015; Chapter 1:1–8.
-
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Vol I. Edition. Beijing: China Medical Science Press. 2020;173.
-
- Yue JY, Chen X, Chen WS. Insights into genus codonopsis: from past achievements to future perspectives. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2023;2023:2242953. - PubMed
-
- Alamgir AD, Vidushi A, Nasseb S, et al. . Recent bioanalytical methods for the isolation of bioactive natural products from genus Codonopsis. Phytochem Analysis. 2023;34:491–506. - PubMed
-
- Ye G, Li C, Huang CG, et al. . The chemical structure of Codonopsis. Chin J Chin Mater Med. 2005;30:1338–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

