Nutraceuticals vs. antibiotic growth promoters: differential impacts on performance, meat quality, blood lipids, cecal microbiota, and organ histomorphology of broiler chicken
- PMID: 38941788
- PMCID: PMC11260365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103971
Nutraceuticals vs. antibiotic growth promoters: differential impacts on performance, meat quality, blood lipids, cecal microbiota, and organ histomorphology of broiler chicken
Abstract
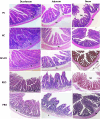
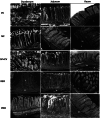
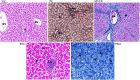
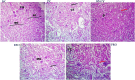
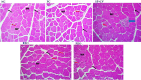
The main goal of this study was to evaluate the effect of nutraceuticals vs. in-feed antibiotics on performance, blood lipids, antioxidant capacity, cecal microbiota, and organ histomorphology of broiler chickens. A total of 320 one-day-old male broiler chickens were distributed into 5 treatment groups with 8 replicates each. The control group was fed on a basal diet without any additives (NC); the antibiotic group was fed on a basal diet supplemented with 100 mg kg-1 avilamycin (PC); the algal group was fed on a basal diet supplemented with a mixture of Spirulina platensis and Chlorella vulgaris (1.5 g + 1.5 g/kg feed) (SP+CV); the essential oil group was fed with a basal diet containing 300 mg/kg feed rosemary oil (REO); and the probiotics group (a mixture of 1 × 1011 CFU/g Bacillus licheniformis, 1 × 1011 CFU/g Enterococcus facieum, 1 × 1010 CFU/g Lactobacillus acidophilus, and 2 × 108 CFU /g Saccharomyces cerevisiae) was fed with a basal diet supplemented with 0.05% probiotics (PRO). The experiment lasted for 35 d. A beneficial effect of SP+CV and PRO (P < 0.01) was noticed on final body weight, body weight gain, feed conversion ratio, and breast yield. The dietary supplementation with SP+CV, REO, and PRO increased (P < 0.001) broilers' cecal lactic acid bacteria count compared to the control. Lower cecal Clostridium perfringens and Coliform counts (P < 0.001) were noticed in chickens fed the PC and supplemental diets. Malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration was decreased, while glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase, and catalase enzymes were increased in the breast and thigh meat (P < 0.001) of broiler chickens fed SP+CV, REO, and PRO diets. Dietary SP+CV, REO, and PRO supplementation decreased (P < 0.001) serum total lipids, cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein, and MDA, but increased serum high-density lipoprotein and GPx compared to PC and NC. No pathological lesions were noticed in the liver, kidney, or breast muscle among broilers. The SP+CV, REO, and PRO groups had greater (P < 0.001) intestinal villi height and crypt depth while lower goblet cell densities (P < 0.01) than the control. The present findings suggest that PRO and SP+CV, followed by REO could be suitable alternatives to in-feed antibiotics for enhancing the performance, health, and meat quality of broiler chickens.
Keywords: antibiotic alternative; broiler chicken; meat quality; nutraceutical; performance.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nano-protected form of rosemary essential oil has a positive influence on blood biochemistry parameters, haematological indices, immune-antioxidant status, intestinal microbiota and histomorphology of meat-type chickens.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104309. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104309. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39303351 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis on the growth performance, antioxidant enzyme activity, nutrient digestibility, cecal microflora, excreta noxious gas emission, and breast meat quality of broiler chickens.Poult Sci. 2018 Jul 1;97(7):2451-2459. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey093. Poult Sci. 2018. PMID: 29672750
-
Influences of Bacillus pumilus SA388 as an environmentally friendly antibiotic alternative on growth performance, blood biochemistry, immunology, cecal microbiota, and meat quality in broiler chickens.Poult Sci. 2024 Nov;103(11):104115. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104115. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39303323 Free PMC article.
-
Productive, internal organ and intestinal histomorphological characteristics of broiler chickens in response to dietary rapeseed meal: A meta-analysis.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2025 Jan;109(1):211-222. doi: 10.1111/jpn.14040. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2025. PMID: 39345033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing broiler growth, health, and meat quality with citric acid- assessing the optimal dose and environmental impact: Citric acid in Broiler Health and Production.Poult Sci. 2025 Feb;104(2):104668. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104668. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39705837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Potential of Silymarin, Spirulina platensis, and Chlorella vulgaris towards Cardiotoxicity via Modulating Antioxidant Activity, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Rats.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;14(10):1289. doi: 10.3390/life14101289. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459589 Free PMC article.
-
Spirulina platensis and Chlorella vulgaris in poultry nutrition - a review of current research and potential opportunities.Poult Sci. 2025 Jun 18;104(9):105456. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105456. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40570455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral supplementation with lactic acid bacteria improve the intestinal epithelial barrier and gut microbiota of broiler chicks to alleviate Salmonella Enteritidis infection.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104385. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104385. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39442198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd El-Hack M.E., El-Saadony M.T., Salem H.M., El-Tahan A.M., Soliman M.M., Youssef G.B.A., Taha A.E., Soliman S.M., Ahmed A.E., El-Kott A.F., Al Syaad K.M., Swelum A.A. Alternatives to antibiotics for organic poultry production: types, modes of action and impacts on bird's health and production. Poult. Sci. 2022;101 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Latif A.S., Saleh N.S., Allam T.S., Ghazy E.W. The effects of rosemary (Rosemarinus afficinalis) and garlic (Allium sativum) essential oils on performance, hematological, biochemical and immunological parameters of broiler chickens. Br. J. Poult. Sci. 2013;2:16–24.
-
- Aberbour, A., L. Touazi, A. Benberkane, S. Aissanou, A. Sherasiya, M. Iguer-Ouada, J.L. Hornick, and N. Moula. 2023. The Effect of in ovo administration of rosemary essential oil on hatchability, relative hatching weight, and embryo mortality rate in Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Animals 13:1217. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Farsi M., Alasalvar C., Morris A., Baron M., Shahidi F. Comparison of antioxidant activity, anthocyanins, carotenoids, and phenolics of three native fresh and sun-dried date (Phoenix Dactylifera L.) varieties grown in Oman. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005;53:7592–7599. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

