Evolutionary and biomedical implications of sex differences in the primate brain transcriptome
- PMID: 38942023
- PMCID: PMC11293591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100589
Evolutionary and biomedical implications of sex differences in the primate brain transcriptome
Abstract
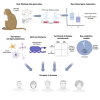
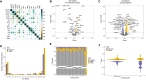
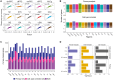
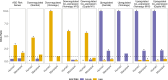
Humans exhibit sex differences in the prevalence of many neurodevelopmental disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we generated one of the largest multi-brain-region bulk transcriptional datasets for the rhesus macaque and characterized sex-biased gene expression patterns to investigate the translatability of this species for sex-biased neurological conditions. We identify patterns similar to those in humans, which are associated with overlapping regulatory mechanisms, biological processes, and genes implicated in sex-biased human disorders, including autism. We also show that sex-biased genes exhibit greater genetic variance for expression and more tissue-specific expression patterns, which may facilitate rapid evolution of sex-biased genes. Our findings provide insights into the biological mechanisms underlying sex-biased disease and support the rhesus macaque model for the translational study of these conditions.
Keywords: animal model; autism; brain evolution; comparative neurobiology; rhesus macaque; sex-biased gene expression.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

