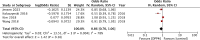Association between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use and diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of real-world studies
- PMID: 38943083
- PMCID: PMC11212248
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-024-03535-1
Association between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use and diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of real-world studies
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this review was to examine if dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP4i) use affects the risk of diabetic retinopathy (DR).
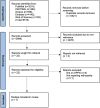
Methods: Cohort studies published up to 20th July 2023 in the databases of PubMed, CENTRAL, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science were searched. The adjusted effect size was pooled to calculate the odds ratio (OR).
Results: Seven studies were included. Meta-analysis showed that the use of DPP4i was not associated with any significant change in the risk of DR (OR: 0.86 95% CI: 0.70, 1.06 I2 = 78%). The pooled analysis also found that DPP4i use was not associated with any significant risk of progression of DR (OR: 0.87 95% CI: 0.47, 1.59 I2 = 86%). The results did not change during sensitivity analysis.
Conclusion: Present evidence from a limited number of real-world studies shows that DPP4i may not affect the incidence and progression of DR. There is a need for further studies from different countries using accurate definitions of DR and its progression to validate the current results.
Keywords: DPP4; Eye; Medications; Microvascular complications; Oral hypoglycemics; Retinopathy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on diabetic retinopathy and its progression: A real-world Korean study.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 28;14(10):e0224549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224549. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31658289 Free PMC article.
-
PROTECTIVE EFFECTS OF DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITORS ON PROGRESSION OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES.Retina. 2016 Dec;36(12):2357-2363. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001098. Retina. 2016. PMID: 27285457
-
Use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors is associated with a lower risk of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021 Jan-Feb;15(1):249-255. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.042. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 33465685
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use and risk of diabetic retinopathy: A population-based study.Diabetes Metab. 2018 Sep;44(4):361-367. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Diabetes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29752167
-
Combination of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 13;8(1):4466. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22658-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29535389 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of long-term use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors with the risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a real-world evidence study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1518545. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1518545. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40308768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong TY, Cheung CMG, Larsen M, Sharma S, Simó R. Diabetic retinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2016;2. 10.1038/NRDP.2016.12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous