PRPF40A induces inclusion of exons in GC-rich regions important for human myeloid cell differentiation
- PMID: 38943321
- PMCID: PMC11347146
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae557
PRPF40A induces inclusion of exons in GC-rich regions important for human myeloid cell differentiation
Abstract
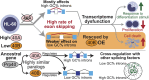
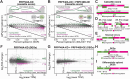
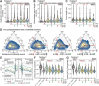
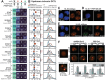
We characterized the regulatory mechanisms and role in human myeloid cell survival and differentiation of PRPF40A, a splicing factor lacking a canonical RNA Binding Domain. Upon PRPF40A knockdown, HL-60 cells displayed increased cell death, decreased proliferation and slight differentiation phenotype with upregulation of immune activation genes. Suggestive of both redundant and specific functions, cell death but not proliferation was rescued by overexpression of its paralog PRPF40B. Transcriptomic analysis revealed the predominant role of PRPF40A as an activator of cassette exon inclusion of functionally relevant splicing events. Mechanistically, the exons exclusively upregulated by PRPF40A are flanked by short and GC-rich introns which tend to localize to nuclear speckles in the nucleus center. These PRPF40A regulatory features are shared with other splicing regulators such as SRRM2, SON, PCBP1/2, and to a lesser extent TRA2B and SRSF2, as a part of a functional network that regulates splicing partly via co-localization in the nucleus.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SRSF2 directly inhibits intron splicing to suppresses cassette exon inclusion.BMB Rep. 2017 Aug;50(8):423-428. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.8.103. BMB Rep. 2017. PMID: 28712387 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between coding and exonic splicing regulatory sequences.Genome Res. 2019 May;29(5):711-722. doi: 10.1101/gr.241315.118. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 30962178 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved role for spliceosomal component PRPF40A in microexon splicing.RNA. 2024 Dec 16;31(1):43-50. doi: 10.1261/rna.080142.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 39389624
-
Targeting serine- and arginine-rich splicing factors to rectify aberrant alternative splicing.Drug Discov Today. 2023 Sep;28(9):103691. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103691. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 37385370 Review.
-
SR Splicing Factors Promote Cancer via Multiple Regulatory Mechanisms.Genes (Basel). 2022 Sep 16;13(9):1659. doi: 10.3390/genes13091659. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CircMAN1A2 Levels Determine GBM Susceptibility to TMZ in a Pathway Involving TEP1- and KEAP1-Mediated NRF2 Degradation Leading to Ferroptosis.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70489. doi: 10.1111/cns.70489. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40583858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng L.G., Liu Z., Kwok I., Ginhoux F.. Origin and heterogeneity of tissue myeloid cells: a focus on GMP-derived monocytes and neutrophils. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023; 41:375–404. - PubMed
-
- Imperato M.R., Cauchy P., Obier N., Bonifer C.. The RUNX1-PU.1 axis in the control of hematopoiesis. Int. J. Hematol. 2015; 101:319–329. - PubMed
-
- Song R., Tikoo S., Jain R., Pinello N., Au A.Y.M., Nagarajah R., Porse B., Rasko J.E.J., J J.L.W. Dynamic intron retention modulates gene expression in the monocytic differentiation pathway. Immunology. 2022; 165:274–286. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

