An Engineered N-Glycosylated Dengue Envelope Protein Domain III Facilitates Epitope-Directed Selection of Potently Neutralizing and Minimally Enhancing Antibodies
- PMID: 38943594
- PMCID: PMC11320570
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00058
An Engineered N-Glycosylated Dengue Envelope Protein Domain III Facilitates Epitope-Directed Selection of Potently Neutralizing and Minimally Enhancing Antibodies
Abstract
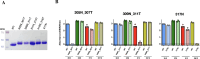
The envelope protein of dengue virus (DENV) is a primary target of the humoral immune response. The domain III of the DENV envelope protein (EDIII) is known to be the target of multiple potently neutralizing antibodies. One such antibody is 3H5, a mouse antibody that binds strongly to EDIII and potently neutralizes DENV serotype 2 (DENV-2) with unusually minimal antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE). To selectively display the binding epitope of 3H5, we strategically modified DENV-2 EDIII by shielding other known epitopes with engineered N-glycosylation sites. The modifications resulted in a glycosylated EDIII antigen termed "EDIII mutant N". This antigen was successfully used to sift through a dengue-immune scFv-phage library to select for scFv antibodies that bind to or closely surround the 3H5 epitope. The selected scFv antibodies were expressed as full-length human antibodies and showed potent neutralization activity to DENV-2 with low or negligible ADE resembling 3H5. These findings not only demonstrate the capability of the N-glycosylated EDIII mutant N as a tool to drive an epitope-directed antibody selection campaign but also highlight its potential as a dengue immunogen. This glycosylated antigen shows promise in focusing the antibody response toward a potently neutralizing epitope while reducing the risk of antibody-dependent enhancement.
Keywords: dengue; domain III; envelope; epitope; glycan; shield.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Dejnirattisai W.; Jumnainsong A.; Onsirisakul N.; Fitton P.; Vasanawathana S.; Limpitikul W.; Puttikhunt C.; Edwards C.; Duangchinda T.; Supasa S.; Chawansuntati K.; Malasit P.; Mongkolsapaya J.; Screaton G. Cross-Reacting Antibodies Enhance Dengue Virus Infection in Humans. Science 2010, 328, 745–748. 10.1126/science.1185181. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beltramello M.; Williams K. L.; Simmons C. P.; Macagno A.; Simonelli L.; Quyen N. T. H.; Sukupolvi-Petty S.; Navarro-Sanchez E.; Young P. R.; de Silva A. M.; Rey F. A.; Varani L.; Whitehead S. S.; Diamond M. S.; Harris E.; Lanzavecchia A.; Sallusto F. The Human Immune Response to Dengue Virus Is Dominated by Highly Cross-Reactive Antibodies Endowed with Neutralizing and Enhancing Activity. Cell Host Microb. 2010, 8, 271–283. 10.1016/j.chom.2010.08.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

