Efficacy of quercetin-like compounds from the mistletoe plant of Dendrophthoe pentandra L. Miq, as oral random blood sugar lowering treatment in diabetic rats
- PMID: 38943615
- PMCID: PMC11216255
- DOI: 10.1080/01652176.2024.2372090
Efficacy of quercetin-like compounds from the mistletoe plant of Dendrophthoe pentandra L. Miq, as oral random blood sugar lowering treatment in diabetic rats
Abstract
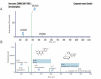
Background: Mistletoe is an herb that grows on duku plants (Lancium demosticum) and is known as benalu duku (BD) in Indonesia. It is predicted to have benefits such as anticancer or antiviral properties, and it is also thought to have anti-diabetic pharmacological activity. Quercetin-like compounds (QLCs) are secondary metabolites with antidiabetic activity that are expected to lower blood sugar levels in animals after oral administration.
Objective: This study aimed to analyze the ability of QLCs to reduce random blood sugar levels using experimental animals as clinical models.
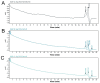
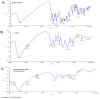
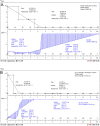
Material and methods: The research method used was exploratory, which used a before-after test model, and observations were made on the random blood sugar levels after treatment. Secondary metabolites were extracted from BD leaves, which were then screened. Diabetes was induced in 30 rats (Rattus norvegicus) by the administration of streptozotocin at 0.045 mg/g body weight daily for 2 days. The antidiabetic effects of the secondary metabolite at doses of 0.5 mg/kg body weight (twice a day) when administered orally for up to 5 days were tested in diabetic rats. The random sugar levels (mg/dL) were measured using a One Touch Ultra Plus medical device for observation of randomized blood sugar levels. Results and novelty: The results revealed that the secondary metabolite, as an analyte from the BD leaf extract, can significantly reduce random blood sugar levels.
Conclusion: The secondary metabolite extracted from BD, could be used to treat diabetes in rats.
Keywords: Benalu duku; Genistein; Health-lifestyle; Insulin; Mistletoe; Morin; Quercetagin; Sugar blood.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro analysis of quercetin-like compounds from mistletoe Dendrophthoe pentandra (L.) Miq as a potential antiviral agent for Newcastle disease.F1000Res. 2024 Jul 23;12:1214. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.133489.8. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38962299 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of an aqueous extract of Chamaerops humilis leaves in obese, hyperglycemic and hyperlipidemic Meriones shawi rats.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2010 Apr;23(2):212-9. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2010. PMID: 20363702
-
Hypoglycemic and antihyperglycemic effect of Ceiba pentandra L. Gaertn in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Ghana Med J. 2013 Sep;47(3):121-7. Ghana Med J. 2013. PMID: 24391227 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-diabetic activity of extract from Persea americana Mill. leaf via the activation of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 May 7;141(1):517-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.03.026. Epub 2012 Mar 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22472105
-
Antidiabetic effects of Olea europaea L. leaves in diabetic rats induced by high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 May 10;235:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.02.001. Epub 2019 Feb 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30721736
Cited by
-
[Quercetin ameliorates myocardial injury in diabetic rats by regulating L-type calcium channels].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Mar 20;45(3):531-541. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.11. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40159968 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Stimulation of Rabbit Squamous Epidermis Cells Using Extracts of Mistletoe Dendrophthoe pentandra L. Miq in a Topical Gel.Vet Med Int. 2025 May 25;2025:4081052. doi: 10.1155/vmi/4081052. eCollection 2025. Vet Med Int. 2025. PMID: 40458480 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin as an Anti-Diabetic Agent in Rodents-Is It Worth Testing in Humans?Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 31;26(15):7391. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157391. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aba PE, Asuzu IU.. 2018. Glycosylated hemoglobin values of alloxan-induced diabetic rats treated with graded doses of Cussonia arborea extract. J Appl Anim Res. 46(1):1478–1482. doi: 10.1080/09712119.2018.1544902. - DOI
-
- Alam S, Sarker MMR, Sultana TN, Chowdhury MNR, Rashid MA, Chaity NI, Zhao C, Xiao J, Hafez EE, Khan SA, et al. . 2022. Antidiabetic phytochemicals from medicinal plants: prospective candidates for new drug discovery and development. Front Endocrinol. 13:800714. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.800714. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- AlShehri MM, AlMeshal MA.. 2020. Pre-column derivatization HPLC method for rapid and sensitive determination of free and total formaldehyde in hair straightening products. Arab J Chem. 13(1):2096–2100. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.03.008. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
