Decoupling Protein Concentration and Aggregate Content Using Diffusion and Water NMR
- PMID: 38943616
- PMCID: PMC11256015
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05875
Decoupling Protein Concentration and Aggregate Content Using Diffusion and Water NMR
Abstract
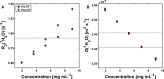
Protein-based biopharmaceutical drugs, such as monoclonal antibodies, account for the majority of the best-selling drugs globally in recent years. For bioprocesses, key performance indicators are the concentration and aggregate level for the product being produced. In water NMR (wNMR), the use of the water transverse relaxation rate [R2(1H2O)] has been previously used to determine protein concentration and aggregate level; however, it cannot be used to separate between them without using an additional technique. This work shows that it is possible to "decouple" these two key characteristics by recording the water diffusion coefficient [D(1H2O)] in conjunction with R2(1H2O), even in the event of overlap in either D(1H2O) or R2(1H2O). This method is demonstrated on three different systems, following appropriate D(1H2O) or R2(1H2O) calibration data acquisition for a protein of interest. Our method highlights the potential use of benchtop NMR as an at-line process analytical technique.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

