Anti-Nociceptive Effect of Sufentanil Polymeric Dissolving Microneedle on Male Mice by Hot Plate Technique
- PMID: 38946039
- PMCID: PMC11444482
- DOI: 10.61186/ibj.4062
Anti-Nociceptive Effect of Sufentanil Polymeric Dissolving Microneedle on Male Mice by Hot Plate Technique
Abstract
Background: Despite the widespread use of opioids to manage severe pain, its systemic administration results in side effects. Among the subcutaneous and transdermal drug delivery systems developed to deal with adverse effects, microneedles have drawn attention due to their rapid action, high drug bioavailability, and improved permeability. Sufentanil (SUF) is an effective injectable opioid for treating severe pain. In this study, we investigated the analgesic effects of SUF using dissolvable microneedles.
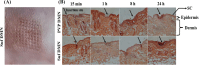
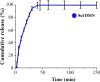
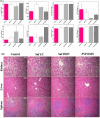
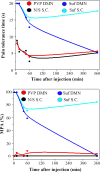
Methods: SUF polymeric dissolvable microneedles were constructed through the mold casting method and characterized by SEM and FTIR analysis. Its mechanical strength was also investigated using a texture analyzer. Fluorescence microscopy was applied in vitro to measure the penetration depth of microneedle arrays. Irritation and microchannel closure time, drug release profile, and hemocompatibility test were conducted for the validation of microneedle efficiency. Hot plate test was also used to investigate the analgesic effect of microneedle in an animal model.
Results: Local administration of SUF via dissolving microneedles had an effective analgesic impact. One hour after administration, there was no significant difference between the subcutaneous and the microneedle groups, and the mechanical properties were within acceptable limits.
Conclusion: Microneedling is an effective strategy in immediate pain relief compared to the traditional methods.
Keywords: Mice; Pain management; Sufentanil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Production of dissolvable microneedles using an atomised spray process: effect of microneedle composition on skin penetration.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014 Feb;86(2):200-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.04.023. Epub 2013 May 29. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014. PMID: 23727511
-
Hard polymeric porous microneedles on stretchable substrate for transdermal drug delivery.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 3;12(1):1853. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05912-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35115643 Free PMC article.
-
Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for rapid and efficient transdermal delivery of insulin to diabetic rats.Acta Biomater. 2013 Nov;9(11):8952-61. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.06.029. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Acta Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23816646
-
Current trends in polymer microneedle for transdermal drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2020 Sep 25;587:119673. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119673. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32739388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissolving microneedles: Applications and growing therapeutic potential.J Control Release. 2022 Aug;348:186-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.045. Epub 2022 Jun 7. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35662577 Review.
Cited by
-
Designing Multifunctional Microneedles in Biomedical Engineering: Materials, Methods, and Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 4;20:8693-8728. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S531898. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40630938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Merskey HJP. Pain terms: a list with definitions and notes on usage Recommended by the IASP Subcommittee on Taxonomy. Pain. 1979;6:249–52. - PubMed
-
- Kerrigan S, Goldberger BA. Principles of forensic toxicology. first ed. Springer; 2020. Opioids. Principles of forensic toxicology; pp. 347–69.
-
- Maurya A, Rangappa S, Bae J, Dhawan T, Ajjarapu SS, Murthy SN. Evaluation of soluble fentanyl microneedles for loco-regional anti-nociceptive activity. Int J Pharm. 2019;564:485–91. - PubMed
-
- Porela-Tiihonen S, Kokki H, Kokki MJEOoP. An up-to-date overview of sublingual sufentanil for the treatment of moderate to severe pain. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020;21(12):1407–18. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Xu W, Xia W, Wei L, Yang D, Deng X, et al. Comparison of the Sedative and Analgesic Effects of dexmedetomidine–remifentanil and dexmedetomidine –dufentanil for liposuction: A prospective single-blind Randomized Controlled Study. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2022;46(1):524–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
