Functional distinction in oncogenic Ras variant activity in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 38946472
- PMCID: PMC11340813
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.050577
Functional distinction in oncogenic Ras variant activity in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
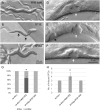
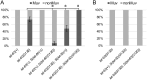
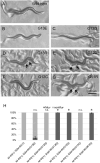
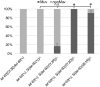
Ras genes are important oncogenes that are frequently mutated in cancer. Human oncogenic variants exhibit functional distinctions in terms of their representation in different cancer types, impact on cellular targets and sensitivity to pharmacological treatments. However, how these distinct variants influence and respond to the cellular networks in which they are embedded is poorly understood. To identify novel participants in the complex interplay between Ras genotype and cell interaction networks in vivo, we have developed and tested an experimental framework using a simple vulva-development assay in the nematode C. elegans. Using this system, we evaluated a set of Ras oncogenic substitution changes at G12, G13 and Q61. We found that these variants fall into distinct groups based on phenotypic differences, sensitivity to gene dosage and inhibition of the downstream kinase MEK and their response to genetic modulators that influence Ras activity in a non-autonomous manner. Together, our results demonstrated that oncogenic C. elegans Ras variants exhibit clear distinctions in how they interface with the vulva-development network and showed that extracellular modulators yield variant-restricted effects in vivo.
Keywords: C. elegans vulva development; Oncogenic Ras variants; Ras/MEK signaling pathway.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Discovery of nonautonomous modulators of activated Ras.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Sep 30;12(10):jkac200. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac200. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35929788 Free PMC article.
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans synthetic multivulva genes prevent ras pathway activation by tightly repressing global ectopic expression of lin-3 EGF.PLoS Genet. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002418. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002418. Epub 2011 Dec 29. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22242000 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of activation of the Caenorhabditis elegans ras homologue let-60 by a novel, temperature-sensitive, gain-of-function mutation.Genetics. 1997 Jun;146(2):553-65. doi: 10.1093/genetics/146.2.553. Genetics. 1997. PMID: 9178006 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans Vulva Induction: An In Vivo Model to Study Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling and Trafficking.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1652:43-61. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7219-7_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28791633 Review.
-
Ras proteins in developmental pattern formation in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila.Semin Cancer Biol. 1992 Aug;3(4):219-28. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992. PMID: 1421166 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

