Gastroesophageal reflux after per-oral endoscopic myotomy: Management literature
- PMID: 38946871
- PMCID: PMC11212704
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i23.2947
Gastroesophageal reflux after per-oral endoscopic myotomy: Management literature
Abstract
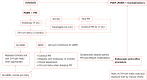
In this editorial, we respond to a review article by Nabi et al, in which the authors discussed gastroesophageal reflux (GER) following peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). POEM is presently the primary therapeutic option for achalasia, which is both safe and effective. A few adverse effects were documented after POEM, including GER. The diagnostic criteria were not clear enough because approximately 60% of patients have a long acid exposure time, while only 10% experience reflux symptoms. Multiple predictors of high disease incidence have been identified, including old age, female sex, obesity, and a baseline lower esophageal sphincter pressure of less than 45 mmHg. Some technical steps during the procedure, such as a lengthy or full-thickness myotomy, may further enhance the risk. Proton pump inhibitors are currently the first line of treatment. Emerging voices are increasingly advocating for the routine combining of POEM with an endoscopic fundoplication method, such as peroral endoscopic fundoplication or transoral incisionless fundoplication. However, more research is necessary to determine the safety and effectiveness of these procedures in the long term for patients who have undergone them.
Keywords: Achalasia; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Per-oral endoscopic myotomy; Peroral endoscopic fundoplication; Transoral incisionless fundoplication.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reflux after peroral endoscopic myotomy: The dilemma and the options.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Feb 14;31(6):100510. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.100510. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39958445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroral endoscopic myotomy vs laparoscopic myotomy and partial fundoplication for esophageal achalasia: A single-center randomized controlled trial.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 7;28(33):4875-4889. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4875. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36156932 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Peroral endoscopic myotomy leads to higher rates of abnormal esophageal acid exposure than laparoscopic Heller myotomy in achalasia.Surg Endosc. 2019 Jul;33(7):2284-2292. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6522-4. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Surg Endosc. 2019. PMID: 30341655
-
Recent progress of gastroesophageal reflux after endoscopic myotomy.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 14;30(34):3926-3928. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3926. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39350788 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux following peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia: Bumps in the road to success.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug 7;30(29):3461-3464. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i29.3461. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39156501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reflux after peroral endoscopic myotomy: The dilemma and the options.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Feb 14;31(6):100510. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.100510. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39958445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Minami H, Inoue H, Haji A, Isomoto H, Urabe S, Hashiguchi K, Matsushima K, Akazawa Y, Yamaguchi N, Ohnita K, Takeshima F, Nakao K. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy: emerging indications and evolving techniques. Dig Endosc. 2015;27:175–181. - PubMed
-
- Chavan R, Nabi Z, Reddy N. Adverse events associated with third space endoscopy: Diagnosis and management. Int J Gastrointest Int. 2020;9
-
- Repici A, Fuccio L, Maselli R, Mazza F, Correale L, Mandolesi D, Bellisario C, Sethi A, Khashab MA, Rösch T, Hassan C. GERD after per-oral endoscopic myotomy as compared with Heller's myotomy with fundoplication: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:934–943.e18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

