The Association Between Neutrophil/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Healthy Population
- PMID: 38946914
- PMCID: PMC11214802
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S464406
The Association Between Neutrophil/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Healthy Population
Abstract
Objective: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by abnormal lipid metabolism and inflammation. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between neutrophil-HDL cholesterol ratio (NHR) and NAFLD in a healthy population.
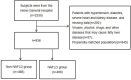
Methods: 1881 healthy people who underwent a physical examination from August to December 2023 at the Hebei General Hospital were chosen for this cross-sectional study. 936 individuals were ultimately included thanks to propensity matching and exclusion criteria. Ultrasound was used to diagnose fatty liver and a t-test or Mann-Whitney test was used to compare the clinical characteristics of participants between groups with and without fatty liver. Logistic regression was used to construct a new model that included NHR. The predictive value of NHR as well as the new model for NAFLD in a healthy population was assessed using logistic regression and subject work characteristic curves.
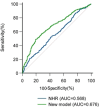
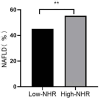
Results: NHR levels were higher among participants in the NAFLD group than those without NAFLD(P<0.05). NHR is a risk factor for NAFLD in a healthy population(P<0.05). The odds ratios (ORs) of NHR for predicting NAFLD in Model I (adjusted for sex, age, and BMI) and Model II (adjusted for sex, age, BMI, HbA1c, TC, TG, and ALT) were 1.166 (1.022, 1.331) and 1.248 (1.110, 1.402)(P<0.05). The new model created by logistic regression predicted NAFLD with an area under the curve of 0.676 (0.645, 0.706). Compared to participants in the low NHR group, the high NHR group exhibited a higher prevalence of NAFLD(p<0.05).
Conclusion: NHR is associated with NAFLD, which is a good predictor of NAFLD in a healthy population.
Keywords: neutrophil/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2024 Jia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: evidence from NHANES 2017-2020.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 15;11:1491858. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1491858. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39882525 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of neutrophil HDL-C ratio - a new inflammation marker in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Endokrynol Pol. 2023;74(6). doi: 10.5603/ep.96715. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Endokrynol Pol. 2023. PMID: 37994581
-
Higher serum uric acid to HDL-cholesterol ratio is associated with onset of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a non-obese Chinese population with normal blood lipid levels.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr 21;22(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02263-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35448944 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum uric acid-to-creatinine ratio and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study in Chinese non-obese people with a normal range of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 14;22(1):419. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02500-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36104672 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of dietary polyphenol supplementation in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 9;13:949746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.949746. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36159792 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
NPR is an independent risk factor for predicting all-cause mortality in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: evidence from NHANES 2007-2020.Popul Health Metr. 2025 Apr 25;23(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12963-025-00378-w. Popul Health Metr. 2025. PMID: 40281626 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of predictive parameters for recurrence in patients undergoing electrical cardioversion for atrial fibrillation.J Arrhythm. 2025 Apr 2;41(2):e70053. doi: 10.1002/joa3.70053. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Arrhythm. 2025. PMID: 40177525 Free PMC article.
-
Association between neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: evidence from NHANES 2017-2020.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 15;11:1491858. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1491858. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39882525 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio predicts deep venous thrombosis in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 14;15(1):25355. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08520-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40659739 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Neutrophil/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study and Predictive Model Construction.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Jul 29;18:2597-2609. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S528506. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40755748 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous