Advances in the role of circulating tumor cell heterogeneity in metastatic small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 38946931
- PMCID: PMC11212323
- DOI: 10.1002/cai2.98
Advances in the role of circulating tumor cell heterogeneity in metastatic small cell lung cancer
Abstract
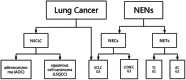
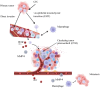
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC), a highly aggressive malignancy, is rapidly at an extensive stage once diagnosed and is one of the leading causes of death from malignancy. In the past decade, the treatment of SCLC has largely remained unchanged, and chemotherapy remains the cornerstone of SCLC treatment. The therapeutic value of adding immune checkpoint inhibitors to chemotherapy for SCLC is low, and only a few SCLC patients have shown a response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are tumor cells shed from solid tumor masses into the peripheral circulation and are key to tumor metastasis. Single-cell sequencing has revealed that the genetic profiles of individual CTCs are highly heterogeneous and contribute to the poor outcome and prognosis of SCLC patients. Theoretically, phenotypic analysis of CTCs may be able to predict the diagnostic significance of new potential targets for metastatic tumors. In this paper, we will discuss in depth the heterogeneity of CTCs in SCLC and the value of CTCs for the diagnosis and prognosis of SCLC and as relevant tumor markers in metastatic SCLC.
Keywords: circulating tumor cell; heterogeneity; immunotherapy; small cell lung cancer; tumor micro‐environment.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Innovation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in predictive biomarkers associated with immunotherapy in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.Cell Biosci. 2024 Sep 12;14(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01283-9. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39267195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of circulating tumor cells in lung cancer: a narrative review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 28;12(4):877-894. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-712. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37197632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Is Liquid Biopsy a New Tool Able to Predict the Efficacy of Immunotherapy?Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 25;14(4):396. doi: 10.3390/biom14040396. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longitudinal detection of subcategorized CD44v6+ CTCs and circulating tumor endothelial cells (CTECs) enables novel clinical stratification and improves prognostic prediction of small cell lung cancer: A prospective, multi-center study.Cancer Lett. 2023 Sep 1;571:216337. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216337. Epub 2023 Aug 6. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 37553013
-
A multicenter pilot study examining the role of circulating tumor cells as a blood-based tumor marker in patients with extensive small-cell lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2014 Oct 14;4:271. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00271. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25353007 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PTPMT1 inhibition induces apoptosis and growth arrest of human SCLC cells by disrupting mitochondrial metabolism.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 31;13(12):6956-6969. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2024-2379. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39816544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nicholson AG, Chansky K, Crowley J, Beyruti R, Kubota K, Turrisi A, et al. The international association for the study of lung cancer lung cancer staging project: proposals for the revision of the clinical and pathologic staging of small cell lung cancer in the forthcoming eighth edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(3):300–311. 10.1016/j.jtho.2015.10.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alix‐Panabières C, Pantel K. Liquid biopsy: from discovery to clinical application. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(4):858–873. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1311 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
