This is a preprint.
Novel Loci (EIF4A2, ADIPOQ, TPRG1) for Triglyceride / High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio Longitudinal Change (ΔTHR) among Subjects without Type 2 Diabetes: Evidence from the Long Life Family Study (LLFS) and the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) Offspring Cohort (OS)
- PMID: 38947029
- PMCID: PMC11213051
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.18.24309120
Novel Loci (EIF4A2, ADIPOQ, TPRG1) for Triglyceride / High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio Longitudinal Change (ΔTHR) among Subjects without Type 2 Diabetes: Evidence from the Long Life Family Study (LLFS) and the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) Offspring Cohort (OS)
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Triglyceride (TG) /High density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio (THR) represents a single surrogate predictor of hyperinsulinemia or insulin resistance that is associated with premature aging processes, risk of diabetes and increased mortality. To identify novel genetic loci for THR change over time (ΔTHR), we conducted genome-wide association study (GWAS) and genome-wide linkage scan (GWLS) among subjects of European ancestry who had complete data from two exams collected about seven years apart from the Long Life Family Study (LLFS, n=1384), a study with familial clustering of exceptional longevity in the US and Denmark.
Methods: Subjects with diabetes or using medications for dyslipidemia were excluded from this analysis. ΔTHR was derived using growth curve modeling, and adjusted for age, sex, field centers, and principal components (PCs). GWAS was conducted using a linear mixed model accounted for familial relatedness. Our linkage scan was built on haplotype-based IBD estimation with 0.5 cM average spacing.
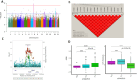
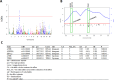
Results: Heritability of ΔTHR was moderate (46%). Our GWAS identified a significant locus at the LPL (p=1.58e-9) for ΔTHR; this gene locus has been reported before influencing baseline THR levels. Our GWLS found evidence for a significant linkage with a logarithm of the odds (LODs) exceeding 3 on 3q28 (LODs=4.1). Using a subset of 25 linkage enriched families (pedigree-specific LODs>0.1), we assessed sequence elements under 3q28 and identified two novel variants (EIF4A2/ADIPOQ-rs114108468, p=5e-6, MAF=1.8%; TPRG1-rs16864075, p=3e-6, MAF=8%; accounted for ~28% and ~29% of the linkage, respectively, and 57% jointly). While the former variant was associated with EIF4A2 (p=7e-5) / ADIPOQ (p=3.49e-2) RNA transcriptional levels, the latter variant was not associated with TPRG1 (p=0.23) RNA transcriptional levels. Replication in FHS OS observed modest effect of these loci on ΔTHR. Of 188 metabolites from 13 compound classes assayed in LLFS, we observed multiple metabolites (e.g., DG.38.5, PE.36.4, TG.58.3) that were significantly associated with the variants (p<3e-4).
Conclusions: our linkage-guided sequence analysis approach permitted our discovery of two novel gene variants EIF4A2/ADIPOQ-rs114108468 and TPRG1-rs16864075 on 3q28 for ΔTHR among subjects without diabetes selected for exceptional survival and healthy aging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel loci for triglyceride/HDL-C ratio longitudinal change among subjects without T2D.J Lipid Res. 2025 Jan;66(1):100702. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100702. Epub 2024 Nov 16. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 39557295 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study identifies common loci influencing circulating glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in non-diabetic subjects: the Long Life Family Study (LLFS).Metabolism. 2014 Apr;63(4):461-8. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.11.018. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24405752 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association study for blood lipid phenotypes in the Framingham Heart Study.BMC Med Genet. 2007 Sep 19;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-S1-S17. BMC Med Genet. 2007. PMID: 17903299 Free PMC article.
-
Gene discovery for high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level change over time in prospective family studies.Atherosclerosis. 2020 Mar;297:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.02.005. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Atherosclerosis. 2020. PMID: 32109663 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association studies identified novel loci for non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and its postprandial lipemic response.Hum Genet. 2014 Jul;133(7):919-30. doi: 10.1007/s00439-014-1435-3. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24604477 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
