This is a preprint.
Differences in HIV-1 reservoir size, landscape characteristics and decay dynamics in acute and chronic treated HIV-1 Clade C infection
- PMID: 38947072
- PMCID: PMC11213047
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.02.16.24302713
Differences in HIV-1 reservoir size, landscape characteristics and decay dynamics in acute and chronic treated HIV-1 Clade C infection
Update in
-
Differences in HIV-1 reservoir size, landscape characteristics, and decay dynamics in acute and chronic treated HIV-1 Clade C infection.Elife. 2025 Feb 20;13:RP96617. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96617. Elife. 2025. PMID: 39976231 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Persisting HIV reservoir viruses in resting CD4 T cells and other cellular subsets are the main barrier to cure efforts. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) intensification by early initiation has been shown to enable post-treatment viral control in some cases but the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. We hypothesized that ART initiated during the hyperacute phase of infection before peak will affect the size, decay dynamics and landscape characteristics of HIV-1 subtype C viral reservoirs.
Methods: We studied 35 women at high risk of infection from Durban, South Africa identified with hyperacute HIV infection by twice weekly testing for plasma HIV-1 RNA. Study participants included 11 who started ART at a median of 456 (297-1203) days post onset of viremia (DPOV), and 24 who started ART at a median of 1 (1-3) DPOV. We used peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to measure total HIV-1 DNA by ddPCR and to sequence reservoir viral genomes by full length individual proviral sequencing (FLIP-seq) from onset of detection of HIV up to 1 year post treatment initiation.
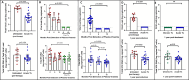
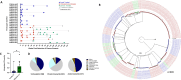
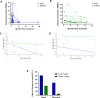
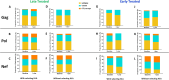
Results: Whereas ART in hyperacute infection blunted peak viremia compared to untreated individuals (p<0.0001), there was no difference in total HIV-1 DNA measured contemporaneously (p=0.104). There was a steady decline of total HIV DNA in early treated persons over 1 year of ART (p=0.0004), with no significant change observed in the late treated group. Total HIV-1 DNA after one year of treatment was lower in the early treated compared to the late treated group (p=0.02). Generation of 697 single viral genome sequences revealed a difference in the longitudinal proviral genetic landscape over one year between untreated, late treated, and early treated infection: the relative contribution of intact genomes to the total pool of HIV-1 DNA after 1 year was higher in untreated infection (31%) compared to late treated (14%) and early treated infection (0%). Treatment initiated in both late and early infection resulted in a more rapid decay of intact (13% and 51% per month) versus defective (2% and 35% per month) viral genomes. However, intact genomes were still observed one year post chronic treatment initiation in contrast to early treatment where intact genomes were no longer detectable. Moreover, early ART reduced phylogenetic diversity of intact genomes and limited the seeding and persistence of cytotoxic T lymphocyte immune escape variants in the reservoir.
Conclusions: Overall, our results show that whereas ART initiated in hyperacute HIV-1 subtype C infection did not impact reservoir seeding, it was nevertheless associated with more rapid decay of intact viral genomes, decreased genetic complexity and immune escape in reservoirs, which could accelerate reservoir clearance when combined with other interventional strategies.
Keywords: Clade C; HIV-1; reservoir; viral dynamics.
Figures
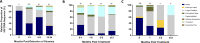
References
-
- Finzi D., Blankson J., Siliciano J.D., Margolick J.B., Chadwick K., Pierson T., Smith K., Lisziewicz J., Lori F., Flexner C., Quinn T.C., Chaisson R.E., Rosenberg E., Walker B., Gange S., Gallant J., and Siliciano R.F., Latent infection of CD4+ T cells provides a mechanism for lifelong persistence of HIV-1, even in patients on effective combination therapy. Nat Med, 1999. 5(5): p. 512–7. - PubMed
-
- Siliciano J.D., Kajdas J., Finzi D., Quinn T.C., Chadwick K., Margolick J.B., Kovacs C., Gange S.J., and Siliciano R.F., Long-term follow-up studies confirm the stability of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells. Nat Med, 2003. 9(6): p. 727–8. - PubMed
-
- Wong J.K., Hezareh M., Gunthard H.F., Havlir D.V., Ignacio C.C., Spina C.A., and Richman D.D., Recovery of replication-competent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science, 1997. 278(5341): p. 1291–5. - PubMed
-
- Deeks S.G., Archin N., Cannon P., Collins S., Jones R.B., de Jong M., Lambotte O., Lamplough R., Ndung’u T., Sugarman J., Tiemessen C.T., Vandekerckhove L., Lewin S.R., and A.S.G.S.S.w.g. International, Research priorities for an HIV cure: International AIDS Society Global Scientific Strategy 2021. Nat Med, 2021. 27(12): p. 2085–2098. - PubMed
-
- Chomont N., El-Far M., Ancuta P., Trautmann L., Procopio F.A., Yassine-Diab B., Boucher G., Boulassel M.R., Ghattas G., Brenchley J.M., Schacker T.W., Hill B.J., Douek D.C., Routy J.P., Haddad E.K., and Sekaly R.P., HIV reservoir size and persistence are driven by T cell survival and homeostatic proliferation. Nat Med, 2009. 15(8): p. 893–900. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
