Identifying Ciliary Proteins in Mammalian Retinas using a Gentle Extraction Method
- PMID: 38947246
- PMCID: PMC11211918
- DOI: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001218
Identifying Ciliary Proteins in Mammalian Retinas using a Gentle Extraction Method
Abstract
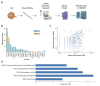
Mutations in retinal primary cilia are responsible for human blindness but the mechanisms are not fully understood (Wheway et al., 2014). Characterizing the proteome of an organelle such as cilia, is a fruitful way to understand its function but methods often require considerable sample quantities. Here we develop a method to isolate the primary cilia of photoreceptor cells from bovine retinas. Through LC/MS/MS proteomics analysis we identify proteins enriched for cilia function including ciliopathy disease. This study shows our method can be used to isolate retinal primary cilia to obtain sufficient quantities of native protein samples.
Copyright: © 2024 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest present.
Figures
References
-
- Drew K, Lee C, Cox RM, Dang V, Devitt CC, McWhite CD, Papoulas O, Huizar RL, Marcotte EM, Wallingford JB. A systematic, label-free method for identifying RNA-associated proteins in vivo provides insights into vertebrate ciliary beating machinery. Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 6;467(1-2):108–117. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.08.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
