Role of Dermatix in the Management of Eyelid Hypertrophic Scars After Facial Trauma
- PMID: 38947592
- PMCID: PMC11214822
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61450
Role of Dermatix in the Management of Eyelid Hypertrophic Scars After Facial Trauma
Abstract
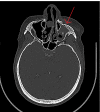
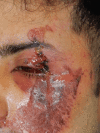
Facial trauma can cause skin wounds with uneven and discoloured edges that require healing by secondary intention. These wounds often produce excess collagen fibres, leading to fibrosis and hypertrophic scars that can cause discomfort and negatively impact the patient's quality of life. A man suffered facial trauma due to a motor vehicle accident, resulting in a fracture of the left zygomatic-maxillary complex. He underwent surgery to fix the fracture and reconstruct his eyelid but developed a hypertrophic scar during recovery that caused eye dryness and discomfort. To treat the scar, Dermatix silicone gel (SG) (Viatris, Canonsburg, PA) was applied twice a day. After two months of treatment, the scar had improved significantly, and the patient's eyelid function had also improved. This case describes the use of Dermatix SG to treat a patient with a traumatic hypertrophic scar of the eyelid associated with eyelid malposition. Silicone gel is a non-invasive treatment for scars and has been shown to be effective in reducing scar elevation and erythema. However, there is a gap in the literature regarding the routine use of SG to preserve functionality and aesthetics in traumatic hypertrophic scars of complex anatomical structures. Further studies are needed to understand the principles of using SG for these types of scars to improve functional and aesthetic outcomes. Applying Dermatix SG twice a day for 60 days corrected a patient's functional and aesthetic issues. More studies should be conducted to investigate the product's effectiveness further.
Keywords: cosmetic outcome; dermatix silicone gel; eyelid elevator; head and neck trauma; hypertrophic scar.
Copyright © 2024, Germano et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The efficacy of topical silicone gel elastomers in the treatment of hypertrophic scars, keloid scars, and post-laser exfoliation erythema.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2007 Sep-Oct;31(5):495-500. doi: 10.1007/s00266-006-0218-1. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2007. PMID: 17700980
-
Real-world management of abnormal scarring using topical silicone gel: expert consensus and case series from the Asian SCARS Expert Group.Drugs Context. 2023 Jul 3;12:2023-4-3. doi: 10.7573/dic.2023-4-3. eCollection 2023. Drugs Context. 2023. PMID: 37415916 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of LeniScar Silicone Stick (AnsCare) With Traditional Silicone Gel (Dermatix Ultra) in Wound Scar Prevention and Removal.Ann Plast Surg. 2023 Apr 1;90(1 Suppl 1):S103-S110. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003393. Ann Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 37075300 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A systematic review of the management of postoperative scars with silicone gel-based products in randomized controlled trials.Dermatol Online J. 2023 Aug 15;29(4). doi: 10.5070/D329461860. Dermatol Online J. 2023. PMID: 37921811
-
Use of tape for the management of hypertrophic scar development: A comprehensive review.Scars Burn Heal. 2021 Jul 12;7:20595131211029206. doi: 10.1177/20595131211029206. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. Scars Burn Heal. 2021. PMID: 34290886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- A systematic review of the management of postoperative scars with silicone gel-based products in randomized controlled trials. Nguyen A, Huynh C, Goh A, Co A, Hassan O, Phan S. Dermatol Online J. 2023;29 - PubMed
-
- Management of eyelid trauma. Nelson CC. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol. 1991;19:357–363. - PubMed
-
- The efficacy of topical silicone gel elastomers in the treatment of hypertrophic scars, keloid scars, and post-laser exfoliation erythema. Chernoff WG, Cramer H, Su-Huang S. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2007;31:495–500. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous