Exploring Unusual Cardiac Complications: Chorda Tendinea Rupture and Pulmonary Valve Vegetation in Infective Endocarditis-A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 38947598
- PMCID: PMC11214664
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61401
Exploring Unusual Cardiac Complications: Chorda Tendinea Rupture and Pulmonary Valve Vegetation in Infective Endocarditis-A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
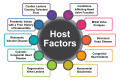
Infective endocarditis (IE) is a severe infection of the endocardium, frequently involving heart valves, and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. At the same time, traditional complications of IE, such as valvular dysfunction and embolic events, are well-documented, and uncommon cardiac manifestations, such as chorda tendinea rupture and pulmonary valve vegetation, present unique diagnostic and management challenges. This comprehensive review explores the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic strategies, and management approaches for IE's chorda tendinea rupture and pulmonary valve vegetation. Through a detailed examination of the literature and discussion of clinical scenarios, we highlight the importance of recognizing these rare complications and discuss the implications for clinical practice. Additionally, we identify knowledge gaps and propose areas for future research to enhance further our understanding and management of these unusual cardiac complications in IE. This review aims to provide clinicians with valuable insights to improve patient care and outcomes in the challenging setting of infective endocarditis.
Keywords: cardiac complications; chorda tendinea rupture; diagnosis; infective endocarditis; management; pulmonary valve vegetation.
Copyright © 2024, Akhil et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Infective endocarditis: practice essentials, background, pathophysiology. [ Apr; 2024 ]. 2024. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/216650-overview https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/216650-overview
-
- Emerging issues in infective endocarditis. Millar BC, Moore JE. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3323180/#:~:text=The%20reas.... Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:1110–1116. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources