Low-coverage whole genome sequencing for a highly selective cohort of severe COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 38948510
- PMCID: PMC11211761
- DOI: 10.46471/gigabyte.127
Low-coverage whole genome sequencing for a highly selective cohort of severe COVID-19 patients
Abstract
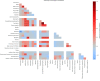
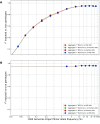
Despite the advances in genetic marker identification associated with severe COVID-19, the full genetic characterisation of the disease remains elusive. This study explores imputation in low-coverage whole genome sequencing for a severe COVID-19 patient cohort. We generated a dataset of 79 imputed variant call format files using the GLIMPSE1 tool, each containing an average of 9.5 million single nucleotide variants. Validation revealed a high imputation accuracy (squared Pearson correlation ≍0.97) across sequencing platforms, showcasing GLIMPSE1's ability to confidently impute variants with minor allele frequencies as low as 2% in individuals with Spanish ancestry. We carried out a comprehensive analysis of the patient cohort, examining hospitalisation and intensive care utilisation, sex and age-based differences, and clinical phenotypes using a standardised set of medical terms developed to characterise severe COVID-19 symptoms. The methods and findings presented here can be leveraged for future genomic projects to gain vital insights into health challenges like COVID-19.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
MC is associated with Cambridge Precision Medicine Ltd. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
