Epidemiology and current management of cerebrovascular disease in China
- PMID: 38948893
- PMCID: PMC11211905
- DOI: 10.26599/1671-5411.2024.05.009
Epidemiology and current management of cerebrovascular disease in China
Abstract
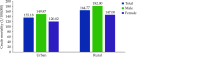
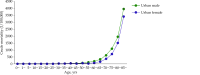
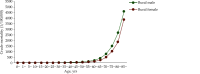
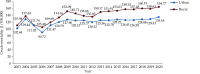
The Annual Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China (2022) intricate landscape of cardiovascular health in China. In connection with the previous section, this fifth section of the report continues the dissection on the management of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Cerebrovascular disease is the leading cause of death and loss of healthy life among Chinese residents. Based on the results of GBD 2019, from 1990 to 2019, the years of life lost due to premature death caused by stroke showed a decreasing trend, while the years lived with disability still increased continuously. At present, national mortality surveillance system can provide national and provincial representative annual death data on cerebrovascular disease, but the national representative data on some other important epidemiological indicators (such as incidence, prevalence, disability rate, and case fatality rate) are scarce in China. With the construction of large cohort population and extension of follow-up time, research on stroke-related risk factors is increasing, providing a basis for the prevention and control of risk factors. Due to limited large-scale population-based intervention studies, there is a lack of epidemiological evidence to transform into feasible intervention strategies and measures. In recent years, great progress in endovascular treatment for basilar-artery occlusion has been achieved in China, but there is still much room for improvement of guideline-based anticoagulant treatment and lipid-lowering treatment, as well as standardized diagnosis and treatment among patients with ischemic stroke.
© 2024 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
China Stroke Statistics 2019: A Report From the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in Neurological Diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, the Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and Institute for Global Neuroscience and Stroke Collaborations.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020 Sep;5(3):211-239. doi: 10.1136/svn-2020-000457. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32826385 Free PMC article.
-
CDC National Health Report: leading causes of morbidity and mortality and associated behavioral risk and protective factors--United States, 2005-2013.MMWR Suppl. 2014 Oct 31;63(4):3-27. MMWR Suppl. 2014. PMID: 25356673
-
Mortality and Morbidity Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Low-Level PM2.5, BC, NO2, and O3: An Analysis of European Cohorts in the ELAPSE Project.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2021 Sep;2021(208):1-127. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2021. PMID: 36106702 Free PMC article.
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
China stroke surveillance report 2021.Mil Med Res. 2023 Jul 19;10(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00463-x. Mil Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37468952 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy, safety, and effect on platelet activation of the timing of administration of tirofiban in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Feb 15;17(2):791-805. doi: 10.62347/JUCB8921. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40092080 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
National Health Commission. China Health Statistics Yearbook 2021; Peking Union Medical College Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
-
-
-
Global Burden Disease 2019. GBD Results. https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/. Access on November 7, 2023.
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
