Dysregulated ribosome quality control in human diseases
- PMID: 38949989
- PMCID: PMC11880988
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.17217
Dysregulated ribosome quality control in human diseases
Abstract
Precise regulation of mRNA translation is of fundamental importance for maintaining homeostasis. Conversely, dysregulated general or transcript-specific translation, as well as abnormal translation events, have been linked to a multitude of diseases. However, driven by the misconception that the transient nature of mRNAs renders their abnormalities inconsequential, the importance of mechanisms that monitor the quality and fidelity of the translation process has been largely overlooked. In recent years, there has been a dramatic shift in this paradigm, evidenced by several seminal discoveries on the role of a key mechanism in monitoring the quality of mRNA translation - namely, Ribosome Quality Control (RQC) - in the maintenance of homeostasis and the prevention of diseases. Here, we will review recent advances in the field and emphasize the biological significance of the RQC mechanism, particularly its implications in human diseases.
Keywords: RQC; proteostasis; ribosome collisions; ribosome quality control; ribosome stalling.
© 2024 The Author(s). The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
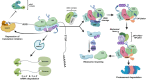
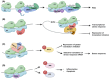
References
-
- Brito Querido J, Díaz‐López I & Ramakrishnan V (2023) The molecular basis of translation initiation and its regulation in eukaryotes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 25, 168–186. - PubMed
-
- Moazed D & Noller HF (1989) Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature 342, 142–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

