Recent advances in gene delivery nanoplatforms based on spherical nucleic acids
- PMID: 38951806
- PMCID: PMC11218236
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02648-5
Recent advances in gene delivery nanoplatforms based on spherical nucleic acids
Abstract
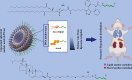
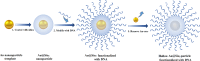
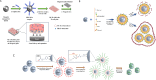
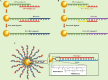
Gene therapy is a therapeutic option for mitigating diseases that do not respond well to pharmacological therapy. This type of therapy allows for correcting altered and defective genes by transferring nucleic acids to target cells. Notably, achieving a desirable outcome is possible by successfully delivering genetic materials into the cell. In-vivo gene transfer strategies use two major classes of vectors, namely viral and nonviral. Both of these systems have distinct pros and cons, and the choice of a delivery system depends on therapeutic objectives and other considerations. Safe and efficient gene transfer is the main feature of any delivery system. Spherical nucleic acids (SNAs) are nanotechnology-based gene delivery systems (i.e., non-viral vectors). They are three-dimensional structures consisting of a hollow or solid spherical core nanoparticle that is functionalized with a dense and highly organized layer of oligonucleotides. The unique structural features of SNAs confer them a high potency in internalization into various types of tissue and cells, a high stability against nucleases, and efficay in penetrating through various biological barriers (such as the skin, blood-brain barrier, and blood-tumor barrier). SNAs also show negligible toxicity and trigger minimal immune response reactions. During the last two decades, all these favorable physicochemical and biological attributes have made them attractive vehicles for drug and nucleic acid delivery. This article discusses the unique structural properties, types of SNAs, and also optimization mechanisms of SNAs. We also focus on recent advances in the synthesis of gene delivery nanoplatforms based on the SNAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



























Similar articles
-
Applications of Spherical Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems.Trends Mol Med. 2019 Dec;25(12):1066-1079. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.08.012. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Trends Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31703931 Review.
-
Spherical Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles: Therapeutic Potential.BioDrugs. 2018 Aug;32(4):297-309. doi: 10.1007/s40259-018-0290-5. BioDrugs. 2018. PMID: 29959665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spherical nucleic acids: emerging amplifiers for therapeutic nanoplatforms.Nanoscale. 2024 Feb 29;16(9):4392-4406. doi: 10.1039/d3nr05971e. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38289178 Review.
-
Therapeutic applications of spherical nucleic acids.Cancer Treat Res. 2015;166:23-50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-16555-4_2. Cancer Treat Res. 2015. PMID: 25895863 Review.
-
Backbone-modified oligonucleotides for tuning the cellular uptake behaviour of spherical nucleic acids.Biomater Sci. 2017 Feb 28;5(3):412-416. doi: 10.1039/c6bm00792a. Biomater Sci. 2017. PMID: 28133665
Cited by
-
Recent advances in nanotechnology for Parkinson's disease: diagnosis, treatment, and future perspectives.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 22;12:1535682. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1535682. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39911864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gold nanoparticles functionalized by phosphine oxide derivatives: characterization and influence of ligand structure on their stability.Nanoscale Adv. 2025 Mar 26;7(11):3255-3266. doi: 10.1039/d5na00111k. eCollection 2025 May 27. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. PMID: 40212454 Free PMC article.
-
The nucleic acid reactions on the nanomaterials surface for biomedicine.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Apr 23;23(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03374-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40269855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photochemical Stabilization of Self-Assembled Spherical Nucleic Acids.Small. 2025 Feb;21(7):e2407742. doi: 10.1002/smll.202407742. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Small. 2025. PMID: 39790078 Free PMC article.
-
Biotechnological advances in microbial synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Optimizations and applications.3 Biotech. 2024 Nov;14(11):263. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04110-7. Epub 2024 Oct 7. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 39387004 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

