Nonlinear association between atherogenic index of plasma and type 2 diabetes mellitus in overweight and obesity patients: evidence from Chinese medical examination data
- PMID: 38951808
- PMCID: PMC11218131
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02330-y
Nonlinear association between atherogenic index of plasma and type 2 diabetes mellitus in overweight and obesity patients: evidence from Chinese medical examination data
Abstract
Background: The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is closely associated with the onset of diabetes, with obesity being a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, the association between the AIP and T2DM in overweight and obese populations has been infrequently studied. Therefore, this study aimed to explore this association in overweight and obese individuals with T2DM.
Methods: This cross-sectional analysis utilized data from 40,633 participants with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 24 kg/m2 who were screened from January 2018 to December 2023 at Henan Provincial People's Hospital. Participants were categorized into groups of overweight and obese individuals with and without diabetes according to the T2DM criteria. The AIP, our dependent variable, was calculated using the formula log10 [(TG mol/L)/HDL-C (mol/L)]. We investigated the association between the AIP and T2DM in overweight and obese individuals using multivariate logistic regression, subgroup analysis, generalized additive models, smoothed curve fitting, and threshold effect analysis. Additionally, mediation analysis evaluated the role of inflammatory cells in AIP-related T2DM.
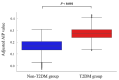
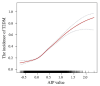
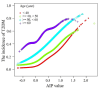
Results: Overweight and obese patients with T2DM exhibited higher AIP levels than those without diabetes. After adjusting for confounders, our results indicated a significant association between the AIP and the risk of T2DM in overweight and obese individuals (odds ratio (OR) = 5.17, 95% confidence interval (CI) 4.69-5.69). Notably, participants with a high baseline AIP (Q4 group) had a significantly greater risk of T2DM than those in the Q1 group, with an OR of 3.18 (95% CI 2.94-3.45). Subgroup analysis revealed that the association between the AIP and T2DM decreased with increasing age (interaction P < 0.001). In overweight and obese populations, the association between AIP and T2DM risk displayed a J-shaped nonlinear pattern, with AIP > - 0.07 indicating a significant increase in T2DM risk. Various inflammatory cells, including neutrophils, leukocytes, and monocytes, mediated 4.66%, 4.16%, and 1.93% of the associations, respectively.
Conclusion: In overweight and obese individuals, the AIP was independently associated with T2DM, exhibiting a nonlinear association. Additionally, the association between the AIP and T2DM decreased with advancing age. Multiple types of inflammatory cells mediate this association.
Keywords: Atherogenic index of plasma; Chinese; Obesity; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baseline atherogenic index of plasma and its trajectory predict onset of type 2 diabetes in a health screened adult population: a large longitudinal study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Feb 7;24(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02619-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39920728 Free PMC article.
-
Atherogenic Index of Plasma (AIP): The Most Accurate Indicator of Overweight and Obesity Among Lipid Indices in Type 2 Diabetes-Findings From a Cross-Sectional Study.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024 Nov;7(6):e70007. doi: 10.1002/edm2.70007. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024. PMID: 39500546 Free PMC article.
-
Threshold effect of atherogenic index of plasma on type 2 diabetes mellitus and modification by uric acid in normal-weight adults with hypertension.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 27;15:1495340. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1495340. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39665019 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of Atherogenic Index of Plasma and other lipid parameters in relation to risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Prim Care Diabetes. 2015 Feb;9(1):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 May 5. Prim Care Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 24810146 Review.
-
The influence of age and overweight or obesity on foot sensitivity and postural control: A systematic review.Australas J Ageing. 2020 Sep;39(3):e251-e258. doi: 10.1111/ajag.12782. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Australas J Ageing. 2020. PMID: 32124534
Cited by
-
Investigation of the relationship between the triglyceride-glucose index and metabolic and hematological parameters in obese individuals.Turk J Med Sci. 2025 Apr 12;55(3):710-718. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.6019. eCollection 2025. Turk J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40686695 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity indices and diabetes risk among hypertensive patients: insights from the China Multi-Ethnicity Cohort study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 10;16:1518060. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1518060. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40130162 Free PMC article.
-
Association of non-traditional lipid indices with diabetes and insulin resistance in US adults: mediating effects of HOMA-IR and evidence from a national cohort.Clin Exp Med. 2025 Aug 7;25(1):281. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01819-4. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40773099 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the atherogenic index of plasma and long-term risk of type 2 diabetes: a 12-year cohort study based on the Japanese population.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 30;24(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02605-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39885511 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary: The atherogenic index of plasma is associated with an increased risk of diabetes in non-obese adults: a cohort study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 17;16:1605942. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1605942. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40747310 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ong KL, Stafford LK, McLaughlin SA, Boyko EJ, Vollset SE, Smith AE, Dalton BE, Duprey J, Cruz JA, Hagins H, Lindstedt PA. Global regional, national burden of diabetes: from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. 2023;402(10397):203–34. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magliano DJ, Boyko EJ. Committee IDFDAtes: IDF Diabetes Atlas. Idf Diabetes Atlas. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation © International Diabetes Federation; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 82071884/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022YFC2010000, 2022YFC2010001/National key research and development plan
- SBGJ202302011, LHGJ20210054/Medical Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province
- 242102311018, 242102311121, 242102310299/Henan Provincial Science and Technology Tackling Program Project Funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

