Management of extensive portal vein thrombosis via thrombolysis and thrombectomy without underlying liver disease: A case report
- PMID: 38952464
- PMCID: PMC11215528
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.8920
Management of extensive portal vein thrombosis via thrombolysis and thrombectomy without underlying liver disease: A case report
Abstract
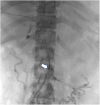
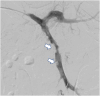
Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is a rare condition, particularly in non-cirrhotic patients. Anticoagulation remains the mainstay of the treatment. Extensive PVT can lead to variceal bleeding, ascites, bowel ischemia, and hypersplenism. The role of thrombolysis and thrombectomy in these patients remains unclear. However, there is evidence that local thrombolysis and thrombectomy should be considered in those who remain symptomatic on anticoagulation and are at risk of complications with acute PVT.
Keywords: anticoagulation; case report; liver cirrhosis; portal vein thrombosis; thrombectomy; thrombolysis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare no actual or potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kalra A, Yetiskul E, Wehrle CJ, Tuma F. Physiology, liver. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2024. - PubMed
-
- Rajani R, Björnsson E, Bergquist A, et al. The epidemiology and clinical features of portal vein thrombosis: a multicentre study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32(9):1154‐1162. - PubMed
-
- Francoz C, Valla D, Durand F. Portal vein thrombosis, cirrhosis, and liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2012;57(1):203‐212. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

