Anti-Infection of Oral Microorganisms from Herbal Medicine of Piper crocatum Ruiz & Pav
- PMID: 38952486
- PMCID: PMC11215520
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S453375
Anti-Infection of Oral Microorganisms from Herbal Medicine of Piper crocatum Ruiz & Pav
Abstract
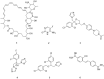
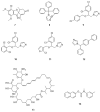
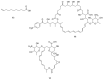
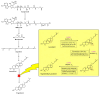
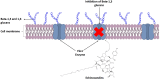
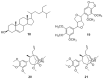
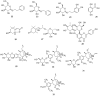
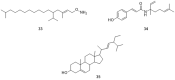
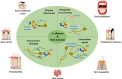
The WHO Global Status Report on Oral Health 2022 reveals that oral diseases caused by infection with oral pathogenic microorganisms affect nearly 3.5 billion people worldwide. Oral health problems are caused by the presence of S. mutans, S. sanguinis, E. faecalis and C. albicans in the oral cavity. Synthetic anti-infective drugs have been widely used to treat oral infections, but have been reported to cause side effects and resistance. Various strategies have been implemented to overcome this problem. Synthetic anti-infective drugs have been widely used to treat oral infections, but they have been reported to cause side effects and resistance. Therefore, it is important to look for safe anti-infective alternatives. Ethnobotanical and ethnopharmacological studies suggest that Red Betel leaf (Piper crocatum Ruiz & Pav) could be a potential source of oral anti-infectives. This review aims to discuss the pathogenesis mechanism of several microorganisms that play an important role in causing health problems, the mechanism of action of synthetic oral anti-infective drugs in inhibiting microbial growth in the oral cavity, and the potential of red betel leaf (Piper crocatum Ruiz & Pav) as an herbal oral anti-infective drug. This study emphasises the importance of researching natural components as an alternative treatment for oral infections that is more effective and can meet global needs.
Keywords: Piper crocatum; anti-infection; antibacterial; antifungal; oral pathogen.
© 2024 Kurnia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

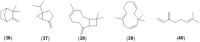
Similar articles
-
Phytochemical Profile of Antibacterial Agents from Red Betel Leaf (Piper crocatum Ruiz and Pav) against Bacteria in Dental Caries.Molecules. 2022 Apr 30;27(9):2861. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092861. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-allergic Inflammatory Components from the Leaves of Piper crocatum Ruiz & Pav.Biol Pharm Bull. 2021;44(2):245-250. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b20-00726. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 33518676
-
Isolation of Two New Compounds and Other Constituents from Leaves of Piper crocatum and Study of Their Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Activities.Molecules. 2019 Jan 30;24(3):489. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030489. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30704047 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial effects of Boesenbergia pandurata and Piper sarmentosum leaf extracts on planktonic cells and biofilm of oral pathogens.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2010 Apr;23(2):224-31. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2010. PMID: 20363704
-
Alkaloids from piper: a review of its phytochemistry and pharmacology.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013 Feb;13(2):163-93. doi: 10.2174/138955713804805148. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23279257 Review.
References
-
- Erlyn P. Efektivitas Antibakteri Fraksi Aktif Serai (Cymbopogon citratus) Terhadap Bakteri Streptococcus mutans. Syifa’ Med J Kedokt Dan Kesehat. 2016;6(2):111. doi:10.32502/Sm.V6i2.1387 - DOI
-
- Ulina N, Turnip MB, Sirait NY, Aminah S, Purba N. Sosialisasi Pemanfaatan Ekstrak Daun Sawo Manila (Manilkara zapota) Sebagai Antibakteri Terhadap Bakteri Streptococcus mutans. Jurnal Pengmas Kestra. 2021;1(2):354–359. doi:10.35451/Jpk.V1i2.899 - DOI
-
- Angga Prawira Kusuma AMT. Description Of Dental Caries In Second Class Students Of Public Elementary School 20 Sungaiselan. Jurnal Pengmas Kestra. 2020;8153:238–244.
-
- Puspitasari N, Widians JA, Budiman E, Wati M, Ramadhan AE. Dayak Onion (Eleutherine palmifolia (L) Merr) As an Alternative Treatment In Early Detection Of Dental Caries Using Certainty Factor. Int Semin Res Inf Technol Intell Syst. 2020;2020(L):482–487. doi:10.1109/ISRITI51436.2020.9315469 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

