A Rare Case of Sublingual Lipoma
- PMID: 38953078
- PMCID: PMC11215033
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61406
A Rare Case of Sublingual Lipoma
Abstract
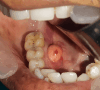
Lipomas are benign soft tissue tumors that are ubiquitous in nature. Available literature suggests that benign tumors are harmless unless they increase in size, resulting in compression of vital structures. This case report discusses the case of a 52-year-old man who presented to the clinic with a painless, growing lump on the right side of his mouth. The patient's symptoms included difficulty swallowing and speaking, which led the doctors to recommend surgical excision of the mass. There were no issues during the mass removal surgery, and the incision healed without compromising the lingual or hypoglossal nerves or Wharton's duct, as observed during follow-up visits. Patient history, symptoms, preoperative examination, treatment strategy, and surgical technique are all included in this case study, which focuses on the extremely unusual development of lipomas in the oral cavity, particularly on the floor of the mouth.
Keywords: adipose tissue; benign tumors; clinical case report; floor of mouth; rare tumors; sublingual lipoma; wharton’s duct.
Copyright © 2024, Shinde et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Ethics Committee, Bharati Vidyapeeth (Deemed to Be University) Dental College and Hospital, Sangli issued approval BV(DU)MC&H/Sangli/IEC/D-40/24. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures





References
-
- Lipoma of the oral and maxillofacial region: site and subclassification of 125 cases. Furlong MA, Fanburg-Smith JC, Childers EL. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004;98:441–450. - PubMed
-
- Lipomas of the oral cavity: clinical findings, histological classification and proliferative activity of 46 cases. Fregnani ER, Pires FR, Falzoni R, Lopes MA, Vargas PA. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;32:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Intraoral lipomas: a clinicopathological study of 43 cases, including four cases of spindle cell/pleomorphic subtype. Linares MF, Leonel AC, Carvalho EJ, de Castro JF, de Almeida OP, Perez DE. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31041916/ Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2019;24:0–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lipoma floor of mouth causing hypoglossal nerve palsy. Zakir I, Zaman SU, Akhtar S, Kulloo P. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020;99:313–315. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
