Structural analysis and blood-enriching effects comparison based on biological potency of Angelica sinensis polysaccharides
- PMID: 38953103
- PMCID: PMC11215113
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1405342
Structural analysis and blood-enriching effects comparison based on biological potency of Angelica sinensis polysaccharides
Abstract
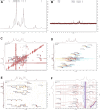
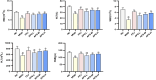
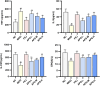
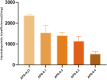
Angelica sinensis is a long-standing medicine used by Chinese medical practitioners and well-known for its blood-tonic and blood-activating effects. Ferulic acid, ligustilide, and eugenol in Angelica sinensis activate the blood circulation; however, the material basis of their blood-tonic effects needs to be further investigated. In this study, five homogeneous Angelica sinensis polysaccharides were isolated, and their sugar content, molecular weight, monosaccharide composition, and infrared characteristics determined. Acetylphenylhydrazine (APH) and cyclophosphamide (CTX) were used as inducers to establish a blood deficiency model in mice, and organ indices, haematological and biochemical parameters were measured in mice. Results of in vivo hematopoietic activity showed that Angelica sinensis polysaccharide (APS) could elevate erythropoietin (EPO), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and interleukin-3 (IL-3) serum levels, reduce tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) level in mice, and promote hematopoiesis in the body by regulating cytokine levels. Biological potency test results of the in vitro blood supplementation indicated strongest tonic activity for APS-H2O, and APS-0.4 has the weakest haemopoietic activity. The structures of APS-H2O and APS-0.4 were characterized, and the results showed that APS-H2O is an arabinogalactan glycan with a main chain consisting of α-1,3,5-Ara(f), α-1,5- Ara(f), β-1,4-Gal(p), and β-1,4-Gal(p)A, and two branched chains of β-t-Gal(p) and α-t-Glc(p) connected to each other in a (1→3) linkage to α-1,3,5-Ara(f) on the main chain. APS-0.4 is an acidic polysaccharide with galacturonic acid as the main chain, consisting of α-1,4-GalA, α-1,2-GalA, α-1,4-Gal, and β-1,4-Rha. In conclusion, APS-H2O can be used as a potential drug for blood replenishment in patients with blood deficiency, providing a basis for APS application in clinical treatment and health foods, as well as research and development of new polysaccharide-based drugs.
Keywords: Angelica sinensis; biological potency; blood tonicity; polysaccharide; structure.
Copyright © 2024 Tian, Shen, Hu, Liang, Ding, Dai, Liu, Lu, Yin, Shu, Guo, Su and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
Author ZG was employed by China Resources Sanjiu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The angelica Polysaccharide: a review of phytochemistry, pharmacology and beneficial effects on systemic diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 May 30;133:112025. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112025. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38677093 Review.
-
Structure characterization and anti-leukemia activity of a novel polysaccharide from Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jan;121:161-172. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.213. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30290264
-
Structures and anti-melanoma activities of two polysaccharides from Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jul 31;183:972-981. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.021. Epub 2021 May 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33965492
-
Leukemia cells apoptosis by a newly discovered heterogeneous polysaccharide from Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels.Carbohydr Polym. 2020 Aug 1;241:116279. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116279. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Carbohydr Polym. 2020. PMID: 32507223
-
Extraction, structure, pharmacological activities and drug carrier applications of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jul 31;183:2337-2353. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.213. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34090852 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological action of Angelica sinensis polysaccharides: a review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 13;15:1510976. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1510976. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39872047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid in situ formation of a double cross-linked network hydrogels for wound healing promotion.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 18;16:1562264. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1562264. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40170721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai T. K., Tian J., Yan B. (2021). Research progress of clinical application and mechanism of action of seven domestic listed polysaccharide drugs. Mod. Traditional Chin. Med. Materia Medica-World Sci. Technol. 23 (10), 3670–3680. 10.11842/wst.20200903003 - DOI
-
- Cao B., Ci Z. M., Xu R. C., Feng B., Xu H., Du X. J., et al. (2020). Quality evaluation of Xiaojin Pills based on antiplatelet aggregation biological potency assay. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.05.022 - DOI
-
- Cao P., Sun J., Sullivan M. A., Huang X., Wang H., Zhang Y., et al. (2018). Angelica sinensis polysaccharide protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury and cell death by suppressing oxidative stress and hepatic apoptosis in vivo and in vitro . Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 111, 1133–1139. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.139 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

