Chemical Standardization of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L.) Extract Using UHPLC-MS/MS and the Method of Standard Addition
- PMID: 38953246
- PMCID: PMC11311221
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.4c00125
Chemical Standardization of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L.) Extract Using UHPLC-MS/MS and the Method of Standard Addition
Abstract
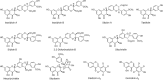
Extracts prepared from the seeds of the medicinal plant milk thistle [Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. (Asteraceae)] are widely used as dietary supplements due to anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and hepatoprotective effects. Called silymarin, the main components of lipophilic extracts of milk thistle seeds are flavonoids and flavonolignans including silybin A, silybin B, isosilybin A, isosilybin B, silydianin, silychristin, taxifolin, and 2,3-dehydrosilybins. The aim of this study was to develop a method based on UHPLC-MS/MS for the chemical authentication and standardization of milk thistle silymarin. Validation included the method of standard addition to account for the lack of a blank matrix. Potential matrix effects were investigated by analyzing silymarin standards dissolved only in the initial UHPLC mobile phase. Measurements of six flavonolignans and taxifolin in the milk thistle extract using UHPLC-MS/MS with standard addition or external standard calibration produced similar results for all analytes except silydianin and 2,3-dehydrosilybin B, which showed significant peak enhancement during negative ion electrospray due to botanical matrix effects. The UHPLC-MS/MS-based method of standard addition requires <10 min per injection and is suitable for the standardization of silymarin from milk thistle in support of preclinical and clinical studies of safety and efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Determination of Flavonolignan Compositional Ratios in Silybum marianum (Milk Thistle) Extracts Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography.Molecules. 2024 Jun 21;29(13):2949. doi: 10.3390/molecules29132949. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38998902 Free PMC article.
-
A validated UHPLC-tandem mass spectrometry method for quantitative analysis of flavonolignans in milk thistle (Silybum marianum) extracts.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Jul 15;126:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.04.028. Epub 2016 Apr 22. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016. PMID: 27136284 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of milk thistle (Silybum marianum) and its main flavonolignans on CYP2C8 enzyme activity in human liver microsomes.Chem Biol Interact. 2017 Jun 1;271:24-29. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.04.025. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Chem Biol Interact. 2017. PMID: 28457856
-
Recent advances in the analysis of flavonolignans of Silybum marianum.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Oct 25;130:301-317. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.05.034. Epub 2016 May 26. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016. PMID: 27321822 Review.
-
The silymarin composition… and why does it matter???Food Res Int. 2017 Oct;100(Pt 3):339-353. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.017. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Food Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28964357 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Plant-Derived Compounds as Novel Perspectives in Oral Cancer Alternative Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 24;18(8):1098. doi: 10.3390/ph18081098. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40872490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marceddu R.; Dinolfo L.; Carrubba A.; Sarno M.; Di Miceli G. Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L.) as a Novel Multipurpose Crop for Agriculture in Marginal Environments: A Review. Agronomy. 2022, 12 (3), 729.10.3390/agronomy12030729. - DOI
-
- Hamilton W. R.; Stohs S.. Hepatic Effects of Herbal Remedies, Chapter 3. In Herbal Medicinals: A Clinician’s Guide; Miller L. G., Murray W. J., Eds.; Pharmaceutical Products Press: New York, 1998; p 37.
-
- Rainone F. Milk Thistle. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 1285–1292. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

