A novel STING variant triggers endothelial toxicity and SAVI disease
- PMID: 38953896
- PMCID: PMC11217899
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20232167
A novel STING variant triggers endothelial toxicity and SAVI disease
Abstract
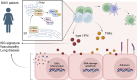
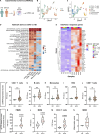
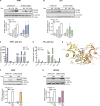
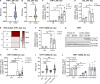
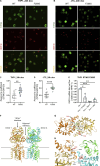
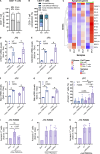
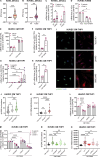
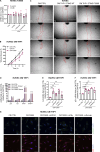
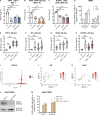
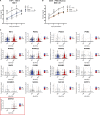
Gain-of-function mutations in STING cause STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy (SAVI) characterized by early-onset systemic inflammation, skin vasculopathy, and interstitial lung disease. Here, we report and characterize a novel STING variant (F269S) identified in a SAVI patient. Single-cell transcriptomics of patient bone marrow revealed spontaneous activation of interferon (IFN) and inflammatory pathways across cell types and a striking prevalence of circulating naïve T cells was observed. Inducible STING F269S expression conferred enhanced signaling through ligand-independent translocation of the protein to the Golgi, protecting cells from viral infections but preventing their efficient immune priming. Additionally, endothelial cell activation was promoted and further exacerbated by cytokine secretion by SAVI immune cells, resulting in inflammation and endothelial damage. Our findings identify STING F269S mutation as a novel pathogenic variant causing SAVI, highlight the importance of the crosstalk between endothelial and immune cells in the context of lung disease, and contribute to a better understanding of how aberrant STING activation can cause pathology.
© 2024 Valeri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

