Advantages of stereolithographic 3D printing in the fabrication of the Affiblot device for dot-blot assays
- PMID: 38954238
- PMCID: PMC11219379
- DOI: 10.1007/s00604-024-06512-z
Advantages of stereolithographic 3D printing in the fabrication of the Affiblot device for dot-blot assays
Abstract
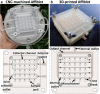
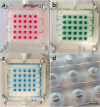
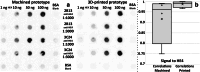
In stereolithographic (SLA) 3D printing, objects are constructed by exposing layers of photocurable resin to UV light. It is a highly user-friendly fabrication method that opens a possibility for technology sharing through CAD file online libraries. Here, we present a prototyping procedure of a microfluidics-enhanced dot-blot device (Affiblot) designed for simple and inexpensive screening of affinity molecule characteristics (antibodies, oligonucleotides, cell receptors, etc.). The incorporation of microfluidic features makes sample processing user-friendly, less time-consuming, and less laborious, all performed completely on-device, distinguishing it from other dot-blot devices. Initially, the Affiblot device was fabricated using CNC machining, which required significant investment in manual post-processing and resulted in low reproducibility. Utilization of SLA 3D printing reduced the amount of manual post-processing, which significantly streamlined the prototyping process. Moreover, it enabled the fabrication of previously impossible features, including internal fluidic channels. While 3D printing of sub-millimeter microchannels usually requires custom-built printers, we were able to fabricate microfluidic features on a readily available commercial printer. Open microchannels in the size range 200-300 μm could be fabricated with reliable repeatability and sealed with a replaceable foil. Economic aspects of device fabrication are also discussed.
Keywords: 3D printing; Antibody; Dot-blot; Microfluidics; Prototyping.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multi-Resin Masked Stereolithography (MSLA) 3D Printing for Rapid and Inexpensive Prototyping of Microfluidic Chips with Integrated Functional Components.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 17;12(8):652. doi: 10.3390/bios12080652. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36005047 Free PMC article.
-
3D Printed Microfluidics.Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2020 Jun 12;13(1):45-65. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-091619-102649. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2020. PMID: 31821017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Custom 3D printer and resin for 18 μm × 20 μm microfluidic flow channels.Lab Chip. 2017 Aug 22;17(17):2899-2909. doi: 10.1039/c7lc00644f. Lab Chip. 2017. PMID: 28726927 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic devices manufacturing with a stereolithographic printer for biological applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021 Oct;129:112388. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112388. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 34579907
-
Vat photopolymerization 3D printed microfluidic devices for organ-on-a-chip applications.Lab Chip. 2023 Aug 8;23(16):3537-3560. doi: 10.1039/d3lc00094j. Lab Chip. 2023. PMID: 37476860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Howat WJ, Lewis A, Jones P, Kampf C, Pontén F, van der Loos CM, Gray N, Womack C, Warford A (2014) Antibody validation of immunohistochemistry for biomarker discovery: recommendations of a consortium of academic and pharmaceutical based histopathology researchers. Methods 70:34–38. 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.01.018 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.01.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Kennedy R, Fitzgerald S, Murphy C (2017) Don’t blame it all on antibodies – the need for exhaustive characterisation, appropriate handling, and addressing the issues that affect specificity. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 89:53–59. 10.1016/j.trac.2017.01.009 10.1016/j.trac.2017.01.009 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/ 16_026/0008446/European Regional Development Fund, Singing Plant
- CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/17_048/ 0007421/OP RDE, Strengthening interdisciplinary cooperation in research of nanomaterials and their effects on living organisms
- RVO 68081715/Ústav analytické chemie, Akademie Věd České Republiky
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
