Effect of tonsillectomy combined with steroid pulse therapy upon IgA nephropathy depending on proteinuria status at diagnosis: a nationwide multicenter cohort study in Japan
- PMID: 38954311
- PMCID: PMC11621197
- DOI: 10.1007/s10157-024-02530-6
Effect of tonsillectomy combined with steroid pulse therapy upon IgA nephropathy depending on proteinuria status at diagnosis: a nationwide multicenter cohort study in Japan
Abstract
Background: The effects of tonsillectomy combined with steroid pulse (TSP) therapy for IgA nephropathy (IgAN) are little known. Therefore, we examined the effects of TSP therapy on the kidney outcomes of IgAN in a large, nationwide cohort study in Japan.
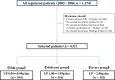
Methods: Between 2002 and 2004, 632 IgAN patients with ≥ 0.5 g/day proteinuria at diagnosis were divided into three groups with mild (0.50-0.99 g/day; n = 264), moderate (1.00-1.99 g/day, n = 216), or severe (≥ 2.00 g/day; n = 153). Decline in kidney function and urinary remission were compared among the three groups after TSP therapy, corticosteroid (ST) therapy, or conservative therapy during a mean follow-up of 6.2 ± 3.3 years. 10.6% and 5.9% of patients in the ST and conservative therapy group underwent tonsillectomy.
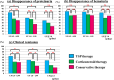
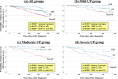
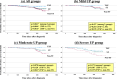
Results: The rate of urinary remission at the final observation was significantly higher in the TSP therapy group than in the ST or conservative therapy groups (mild proteinuria: 64%, 43%, and 41%; moderate proteinuria: 51%, 45%, and 28%; severe proteinuria: 48%, 30%, and 22%, respectively). In contrast, the rate of a 50% increase in serum creatinine was lower in groups TSP therapy, than ST or conservative therapy (mild proteinuria: 2.1%, 10.1% and 16.7%; moderate proteinuria: 4.8%, 8.8% and 27.7%; severe proteinuria: 12.0%, 28.9% and 43.1%, respectively). In multivariate analysis, TSP therapy significantly prevented a 50% increase in serum creatinine levels compared with conservative therapy in groups with moderate and severe proteinuria (hazard ratio, 0.12 and 0.22, respectively).
Conclusion: TSP significantly increased the rate of proteinuria disappearance and urinary remission in IgAN patients with mild-to-moderate urinary protein levels. It may also reduce the decline in kidney function in patients with moderate-to-severe urinary protein levels.
Keywords: Glomerulonephritis; IgA nephropathy; Kidney outcome; Proteinuria; Steroid pulse therapy; Tonsillectomy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: All the authors have declared no competing interest. Ethical approval: All the procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee at which the studies were conducted and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significance of tonsillectomy combined with steroid pulse therapy for IgA nephropathy with mild proteinuria.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016 Feb;20(1):94-102. doi: 10.1007/s10157-015-1138-7. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26123429 Free PMC article.
-
Tonsillectomy and steroid pulse (TSP) therapy for patients with IgA nephropathy: a nationwide survey of TSP therapy in Japan and an analysis of the predictive factors for resistance to TSP therapy.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2009 Oct;13(5):460-466. doi: 10.1007/s10157-009-0179-1. Epub 2009 May 19. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19449181
-
Comparison of oral steroids with tonsillectomy plus steroid pulse therapy in patients with IgA nephropathy.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017 Aug;21(4):617-623. doi: 10.1007/s10157-016-1324-2. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27549901
-
Tonsillectomy combined with steroid pulse therapy induces clinical remission of IgA nephropathy.Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;72:57-9. doi: 10.1159/000324606. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011. PMID: 21865690 Review.
-
A treatment dilemma in adult immunoglobulin A nephropathy: what is the appropriate target, preservation of kidney function or induction of clinical remission?Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012 Apr;16(2):195-201. doi: 10.1007/s10157-011-0552-8. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22086123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- D’Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987;64:709–27. - PubMed
-
- Julian BA, Waldo FB, Rifai A, Mestecky J. IgA nephropathy, the most common glomerulonephritis worldwide. A neglected disease in the United States? Am J Med. 1988;84:129–32. - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama H, Yokoyama H, Sato H, Saito T, Kohda Y, Nishi S, Tsuruya K, Kiyomoto H, Iida H, Sasaki T, Higuchi M, Hattori M, Oka K, Kagami S, Nagata M, Kawamura T, Honda M, Fukasawa Y, Fukatsu A, Morozumi K, Yoshikawa N, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S, Kiyohara Y, Joh K, Taguchi T, Makino H, Committee for Standardization of Renal Pathological Diagnosis, Working Group for Renal Biopsy Database, Japanese Society of Nephrology. Japan Renal Biopsy Registry: the first nationwide, web-based, and prospective registry system of renal biopsies in Japan. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011;15:493–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

