Iron gallic acid biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 38954698
- PMCID: PMC11218937
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306142
Iron gallic acid biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
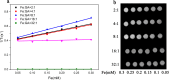
Developing T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents with enhanced biocompatibility and targeting capabilities is crucial owing to concerns over current agents' potential toxicity and suboptimal performance. Drawing inspiration from "biomimetic camouflage," we isolated cell membranes (CMs) from human glioblastoma (T98G) cell lines via the extrusion method to facilitate homotypic glioma targeting. At an 8:1 mass ratio of ferric chloride hexahydrate to gallic acid (GA), the resulting iron (Fe)-GA nanoparticles (NPs) proved effective as a T1-weighted MRI contrast agent. T98G CM-coated Fe-GA NPs demonstrated improved homotypic glioma targeting, validated through Prussian blue staining and in vitro MRI. This biomimetic camouflage strategy holds promise for the development of targeted theranostic agents in a safe and effective manner.
Copyright: © 2024 Chen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Fu CK, Yu Y, XU X, et al.. Functional polymers as metal-free magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Progress in Polymer Science, 2020, 108, 101286. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2020.101286 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

