Protein modification and degradation in ferroptosis
- PMID: 38955112
- PMCID: PMC11267077
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103259
Protein modification and degradation in ferroptosis
Abstract
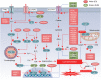
Ferroptosis is a form of iron-related oxidative cell death governed by an integrated redox system, encompassing pro-oxidative proteins and antioxidative proteins. These proteins undergo precise control through diverse post-translational modifications, including ubiquitination, phosphorylation, acetylation, O-GlcNAcylation, SUMOylation, methylation, N-myristoylation, palmitoylation, and oxidative modification. These modifications play pivotal roles in regulating protein stability, activity, localization, and interactions, ultimately influencing both the buildup of iron and lipid peroxidation. In mammalian cells, regulators of ferroptosis typically undergo degradation via two principal pathways: the ubiquitin-proteasome system, which handles the majority of protein degradation, and autophagy, primarily targeting long-lived or aggregated proteins. This comprehensive review aims to summarize recent advances in the post-translational modification and degradation of proteins linked to ferroptosis. It also discusses strategies for modulating ferroptosis through protein modification and degradation systems, providing new insights into potential therapeutic applications for both cancer and non-neoplastic diseases.
Keywords: Autophagy; Degradation; Ferroptosis; Modification; Proteasome.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D.W., Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M., Antonov A.V., Arama E., Baehrecke E.H., Barlev N.A., Bazan N.G., Bernassola F., Bertrand M.J.M., Bianchi K., Blagosklonny M.V., Blomgren K., Borner C., Boya P., Brenner C., Campanella M., Candi E., Carmona-Gutierrez D., Cecconi F., Chan F.K., Chandel N.S., Cheng E.H., Chipuk J.E., Cidlowski J.A., Ciechanover A., Cohen G.M., Conrad M., Cubillos-Ruiz J.R., Czabotar P.E., D'Angiolella V., Dawson T.M., Dawson V.L., De Laurenzi V., De Maria R., Debatin K.M., DeBerardinis R.J., Deshmukh M., Di Daniele N., Di Virgilio F., Dixit V.M., Dixon S.J., Duckett C.S., Dynlacht B.D., El-Deiry W.S., Elrod J.W., Fimia G.M., Fulda S., Garcia-Saez A.J., Garg A.D., Garrido C., Gavathiotis E., Golstein P., Gottlieb E., Green D.R., Greene L.A., Gronemeyer H., Gross A., Hajnoczky G., Hardwick J.M., Harris I.S., Hengartner M.O., Hetz C., Ichijo H., Jaattela M., Joseph B., Jost P.J., Juin P.P., Kaiser W.J., Karin M., Kaufmann T., Kepp O., Kimchi A., Kitsis R.N., Klionsky D.J., Knight R.A., Kumar S., Lee S.W., Lemasters J.J., Levine B., Linkermann A., Lipton S.A., Lockshin R.A., Lopez-Otin C., Lowe S.W., Luedde T., Lugli E., MacFarlane M., Madeo F., Malewicz M., Malorni W., Manic G., Marine J.C., Martin S.J., Martinou J.C., Medema J.P., Mehlen P., Meier P., Melino S., Miao E.A., Molkentin J.D., Moll U.M., Munoz-Pinedo C., Nagata S., Nunez G., Oberst A., Oren M., Overholtzer M., Pagano M., Panaretakis T., Pasparakis M., Penninger J.M., Pereira D.M., Pervaiz S., Peter M.E., Piacentini M., Pinton P., Prehn J.H.M., Puthalakath H., Rabinovich G.A., Rehm M., Rizzuto R., Rodrigues C.M.P., Rubinsztein D.C., Rudel T., Ryan K.M., Sayan E., Scorrano L., Shao F., Shi Y., Silke J., Simon H.U., Sistigu A., Stockwell B.R., Strasser A., Szabadkai G., Tait S.W.G., Tang D., Tavernarakis N., Thorburn A., Tsujimoto Y., Turk B., Vanden Berghe T., Vandenabeele P., Vander Heiden M.G., Villunger A., Virgin H.W., Vousden K.H., Vucic D., Wagner E.F., Walczak H., Wallach D., Wang Y., Wells J.A., Wood W., Yuan J., Zakeri Z., Zhivotovsky B., Zitvogel L., Melino G., Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dixon S.J., Lemberg K.M., Lamprecht M.R., Skouta R., Zaitsev E.M., Gleason C.E., Patel D.N., Bauer A.J., Cantley A.M., Yang W.S., Morrison B., 3rd, Stockwell B.R. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dai E., Han L., Liu J., Xie Y., Kroemer G., Klionsky D.J., Zeh H.J., Kang R., Wang J., Tang D. Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis drives tumor-associated macrophage polarization via release and uptake of oncogenic KRAS protein. Autophagy. 2020;16:2069–2083. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1714209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

